Whole body MRI and 50+ blood tests
This is a comprehensive health check that combines a whole body MRI, 50+ advanced blood tests and a personal medical assessment. The examination provides a reliable overview of your health and makes it possible to detect risks and deviations at an early stage – often before symptoms have developed. The aim is to give you security, prevent illness and create the best conditions for a long and healthy life. You will receive medical contact both before and after the examination, a written medical report, digital access to all MRI images and a personal conversation where the results are explained and the next steps are discussed. If necessary, a rapid referral for further care will be made.
Whole body MRI
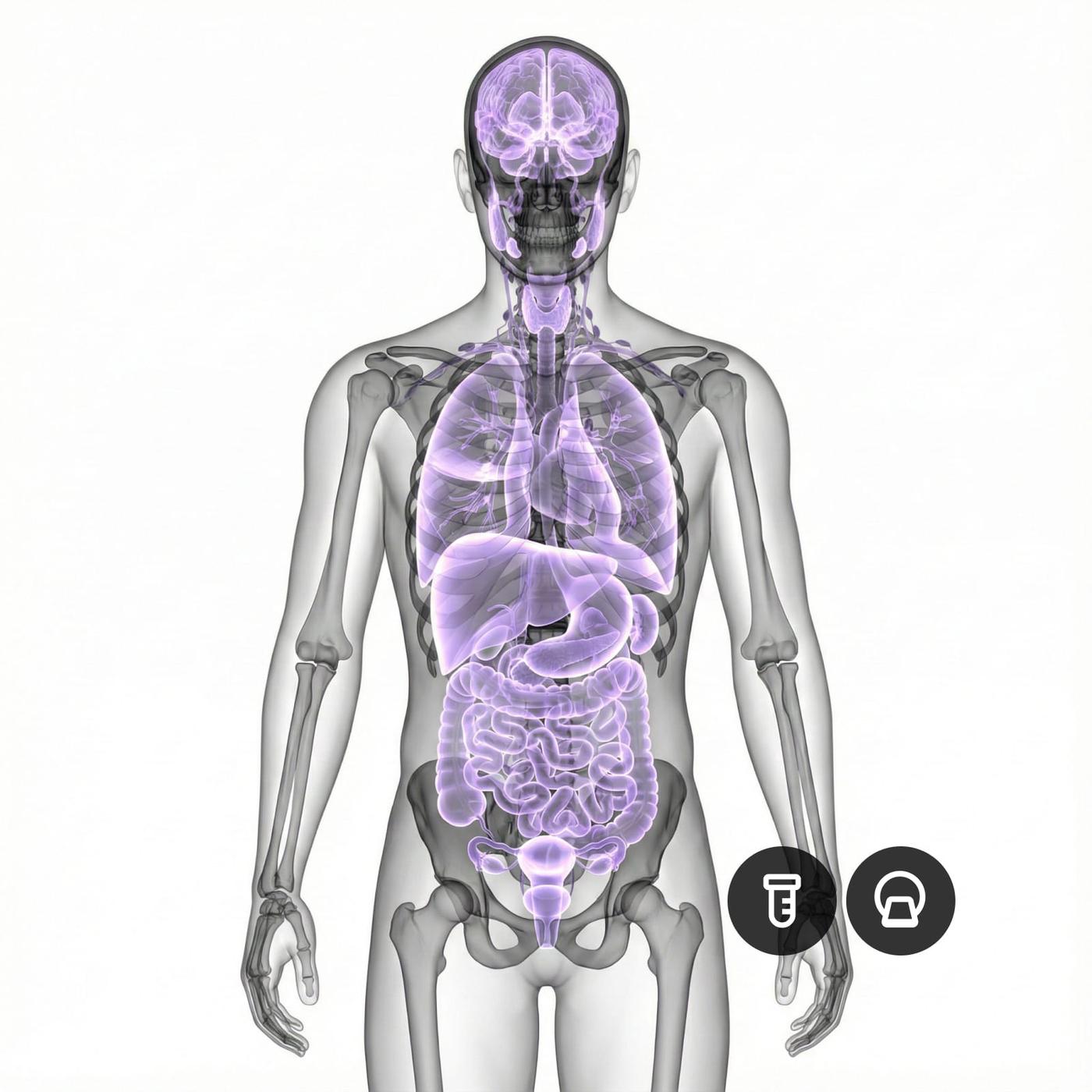
The examination is carried out with a 50–60 minute full body scan at Evidia. The radiologist examines images and sequences of your brain, internal organs, aorta, neck, thoracic spine, spine, pelvis and skeleton in detail to identify any changes such as tumors, cysts, aneurysms, inflammation or early signs of degenerative diseases. The examination is completely radiation-free, which makes the method safe even for preventive use. Afterwards, you have access to all MRI images digitally, which provides full transparency and the opportunity to use the material in future healthcare contacts. In this way, whole-body MRI becomes an effective tool for early detection and safe preventive care.
50 blood tests and biological age
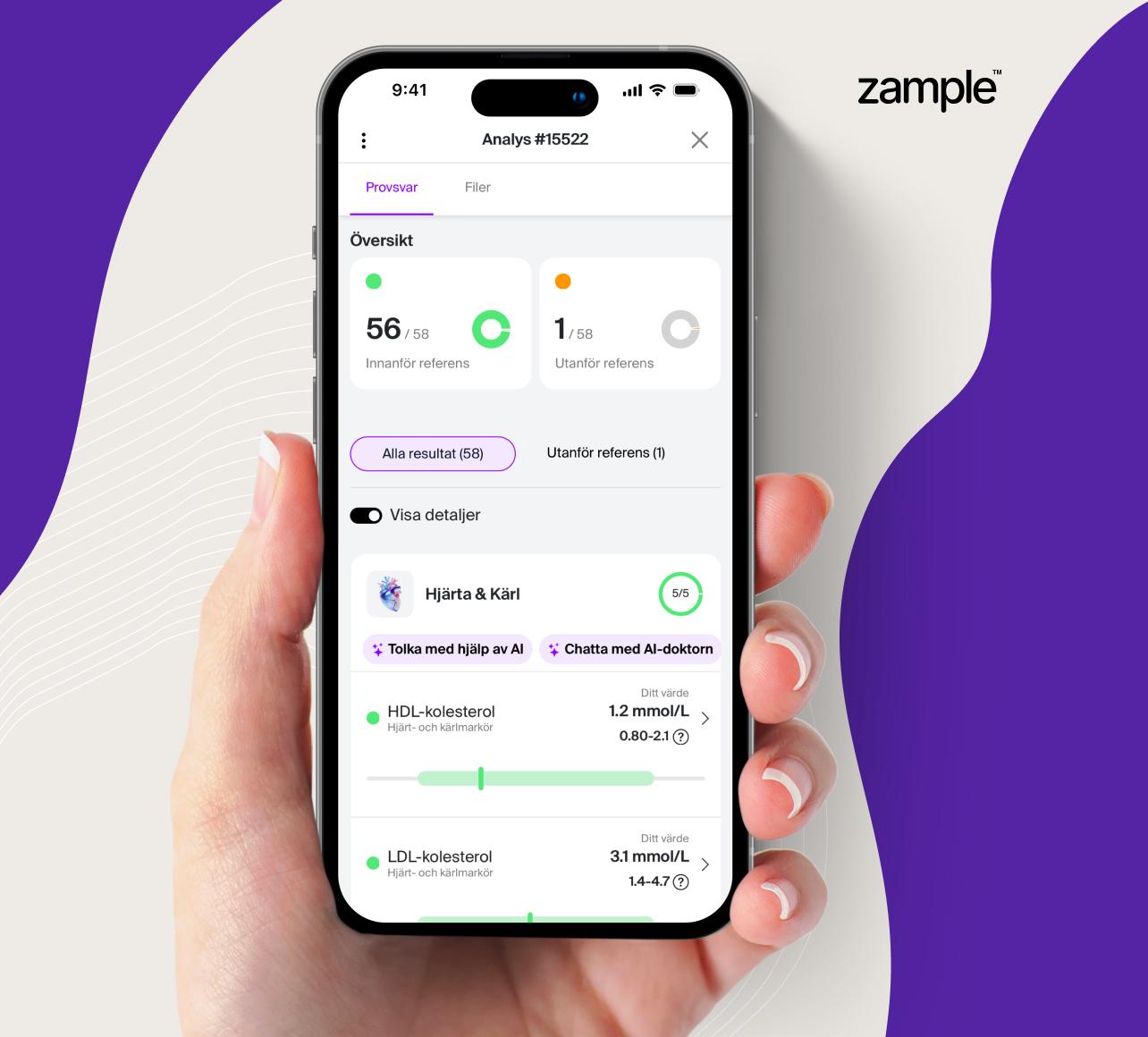
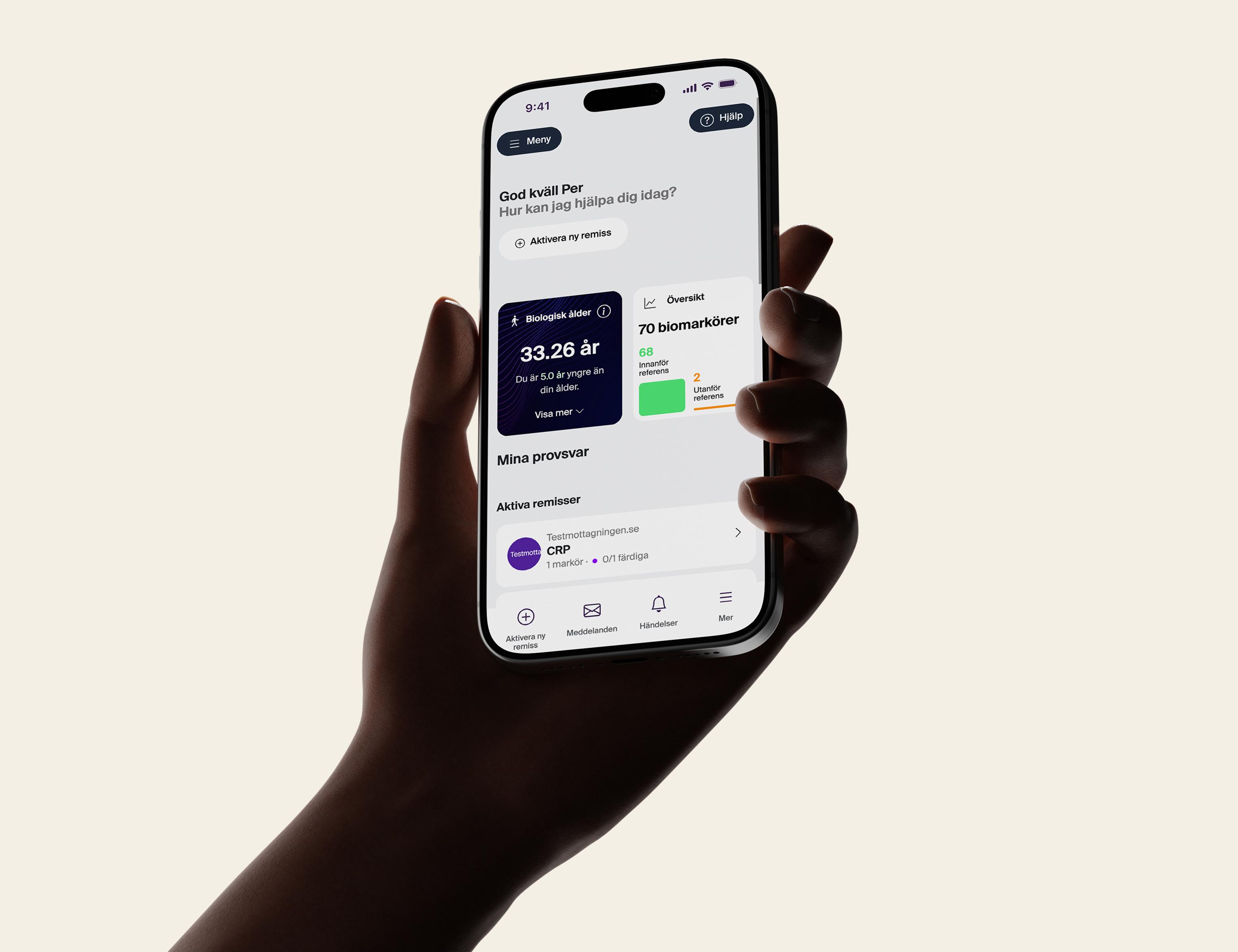
The examination also includes over 50 blood tests that cover key areas of your general health. These include markers for cardiovascular risk, hormones, thyroid function, liver and kidney health, diabetes, vitamins and minerals, stress levels and inflammatory processes. Together, the test results provide a detailed picture of how your body is doing on the inside and can reveal abnormalities that are not always detected until symptoms develop. The results are also supplemented with a calculation of your biological age – a measure of how your body functions in practice compared to your actual age.
Doctor's contact before and after
- Review of health declaration and your questions prior to examination.
- Written medical report, digital MRI images and personal conversation.
- Further referral in the event of pathological findings or abnormalities.
Everything in a comprehensive assessment
Several medical perspectives are integrated into a single analysis. Whole-body MRI provides a radiological mapping of the brain, organs, blood vessels and skeleton, while over 50 laboratory analyses provide insight into biochemical processes related to the heart, blood vessels, hormones, metabolism, kidneys, liver and immune system. When these findings are put in relation to your medical history and health background, a multidimensional and clinically relevant overall picture of your health is created. This makes it possible to detect early pathological changes, identify risk factors and interpret laboratory abnormalities in their clinical context. The doctor can thus see the relationship between blood values and imaging findings, discover patterns that otherwise risk being overlooked and provide medical recommendations tailored specifically to you. The comprehensive check-up thus becomes a powerful tool for early intervention and to prevent future disease development.
Benefits of a preventive comprehensive check-up
- Early detection of disease – often before symptoms are noticed.
- Comprehensive picture through a combination of MRI, blood tests and medical history.
- Personal doctor contact both before and after the examination.
- Written report and digital access to MRI images.
- Relevant advice and referral if necessary.
Do you want to deepen your heart check-up?
- Ultrasound of the heart (echocardiography): assesses the structure and pumping ability of the heart.
- Long-term ECG at home: records the heart rhythm over several days to detect rhythm disturbances.