Arsenic test - Venous blood test to measure your arsenic levels
This analysis measures the concentration of arsenic in the blood and is used to assess your exposure to arsenic. The arsenic test is particularly useful for detecting potentially harmful levels of inorganic arsenic, which can cause serious health problems with prolonged exposure. Inorganic arsenic can be found in contaminated drinking water and certain foods, such as rice. Elevated arsenic levels in the body have been linked to cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and nerve damage. By analyzing the arsenic levels in the blood, this test can help identify potential risks and lead to preventive measures.
Uses of the arsenic analysis
Arsenic tests are used in several clinical situations where it is important to assess exposure to this toxic metal. Common conditions or evaluations where the test is recommended include:
- Suspected arsenic poisoning to evaluate exposure from contaminated drinking water, occupational environments, or specific foods that may contain high levels of arsenic.
- Investigation of industrial exposure individuals working in industries where arsenic is used or produced may be at higher risk of exposure.
- Monitoring chronic arsenic exposure prolonged exposure to arsenic can lead to serious health risks, such as cancer, and monitoring arsenic levels can be crucial in preventing complications.
- Health check in high-risk areas people living in areas where drinking water is contaminated with arsenic should regularly test their arsenic levels to ensure they remain within safe limits.
When is an arsenic test recommended?
An analysis of arsenic concentration is recommended when there is suspicion of exposure from contaminated drinking water, food, occupational environments, or other potential sources. It is particularly relevant for individuals living in high-risk areas or those exposed to arsenic through their work. The test is based on venous blood sampling and provides reliable results for detecting increased arsenic exposure. Combining arsenic measurement with other relevant tests can provide a comprehensive picture of an individual’s exposure and the need for preventive actions.
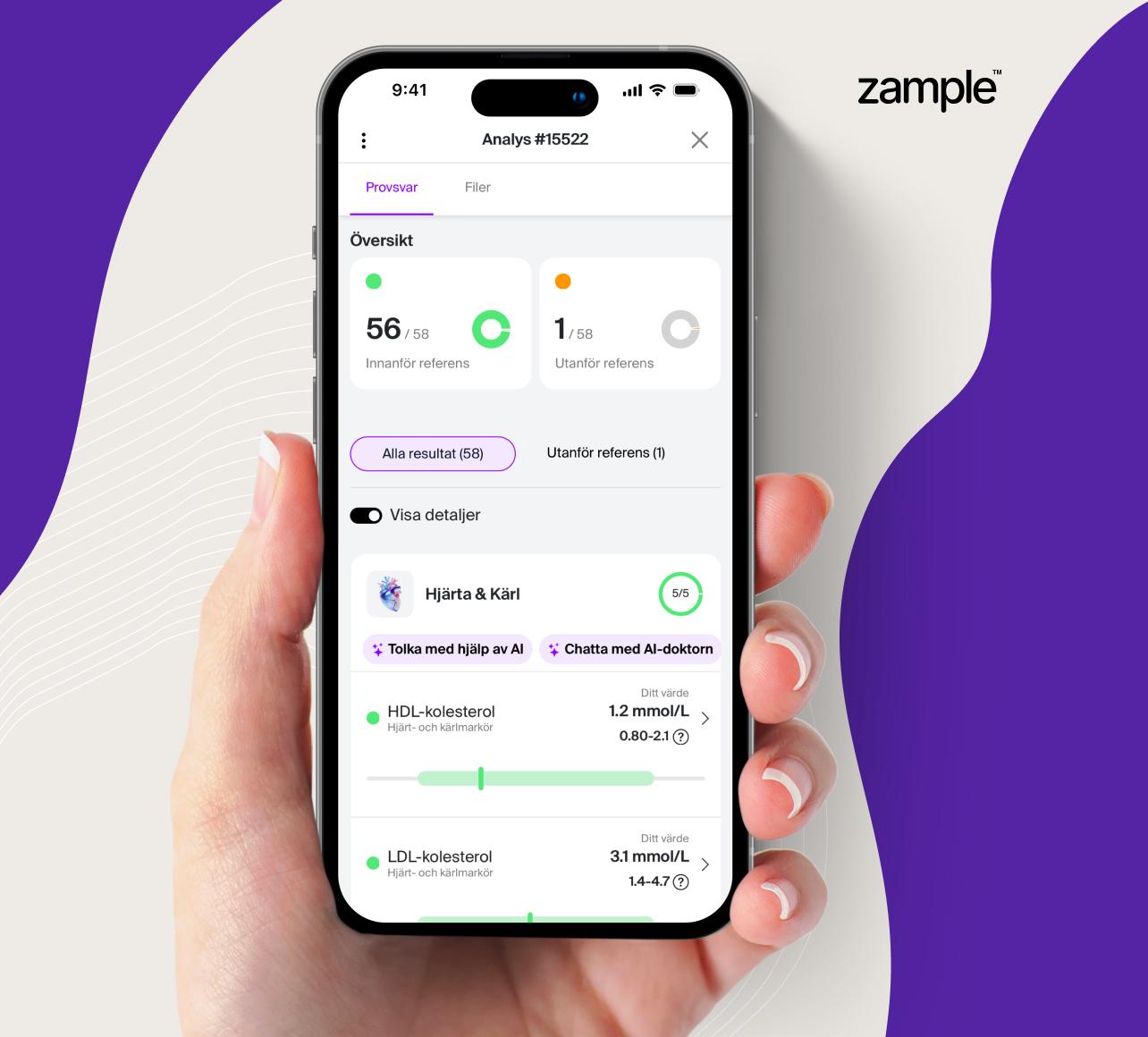
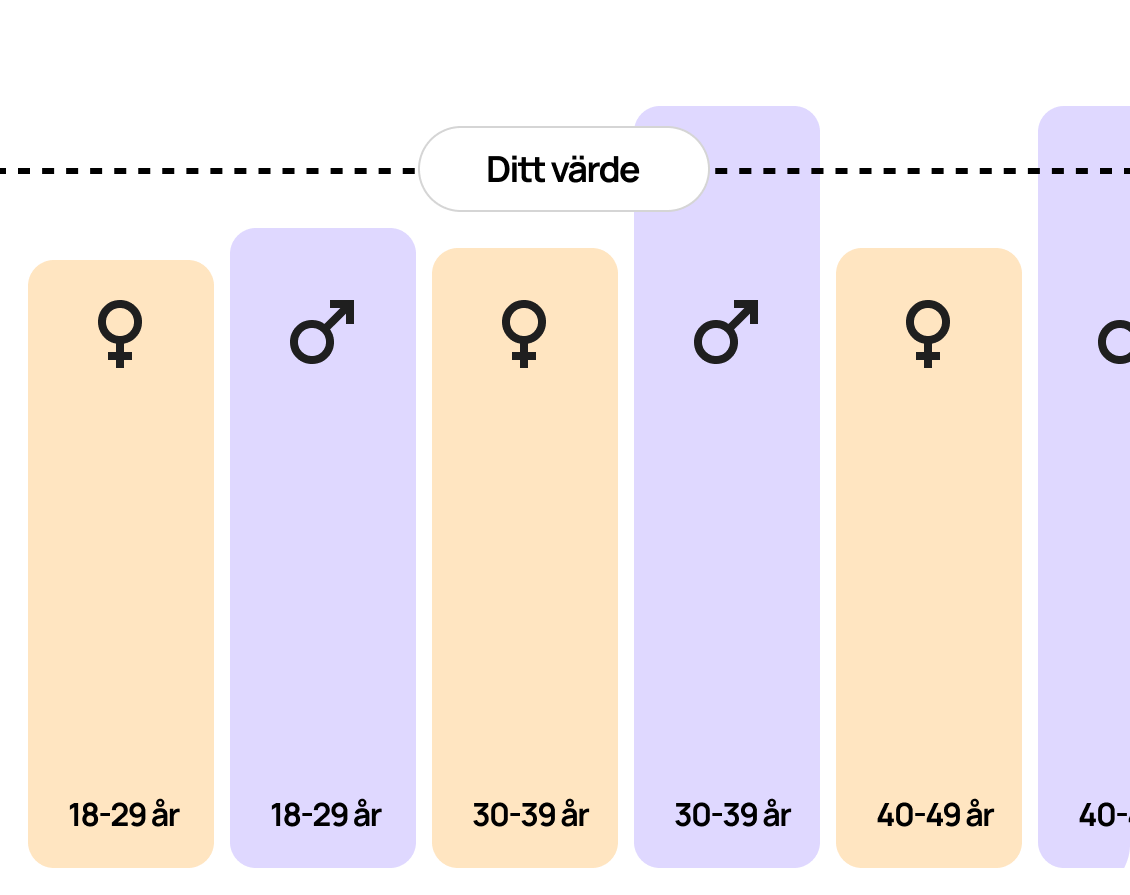
Reference range for Arsenic (B-)
Normal reference values for arsenic in the blood (P-Arsenic) are typically between 0.01–0.05 µmol/L in individuals without known exposure. Levels above 0.67 µmol/L (equivalent to 50 µg/L) may indicate increased exposure and should be further investigated to determine possible sources of arsenic exposure and associated health risks. It is important to note that reference values may vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the analytical method used.
Interpretation of arsenic analysis results
A normal reference range for arsenic in the blood is between 0.01 and 0.05 µmol/L. Elevated arsenic levels may indicate exposure from sources such as contaminated water, certain foods, or occupational environments involving arsenic. For levels above 0.67 µmol/L, further investigation should be conducted to identify potential causes of exposure. Arsenic poisoning can lead to serious health problems, and at high levels, actions should be taken to reduce exposure.