Cardiovascular disease is one of our most common public diseases. The job of the heart and vascular system is to pump the blood around to ensure that all the organs get the nutrition they need. But sometimes imbalances can occur that can lead to serious health problems, especially when it comes to cardiovascular disease. High blood fats and high blood sugar are risk factors that we should follow up on a regular basis to avoid illness in the long term.
Take control of your cardiovascular health
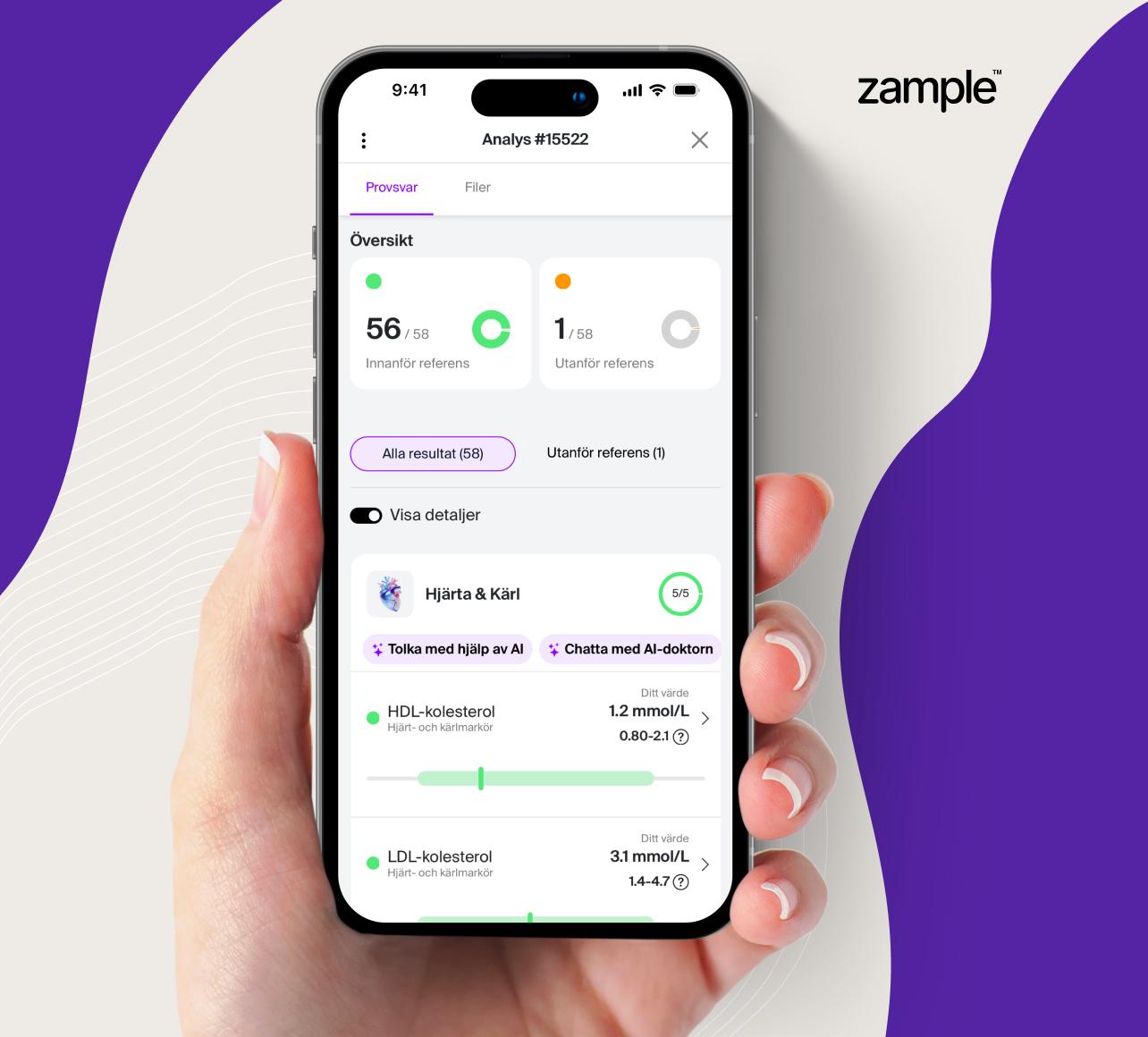
To give you a complete picture of your cardiovascular health, we recommend our "Heart & Vessels" health test. This test carefully analyzes several important biomarkers in your blood, which gives you an insight into your blood status as well as a good prerequisite for assessing your risk profile for possible cardiovascular diseases. By checking your cardiovascular health, you can ensure that your values are within the reference range and that you have the prerequisites for a sound and healthy health.
Biomarkers included in the test
- Erythrocytes: The number of red blood cells that transport oxygen to organs and tissues.
- Erythrocyte average cell volume: Measures the size of red blood cells, provides information about anemia or blood disorders.
- Hematocrit: The proportion of red blood cells in the blood, gives insight into blood density.
- Hemoglobin: Protein in red blood cells that binds oxygen, assesses oxygen transport capacity.
- Hemoglobin mass: Total hemoglobin in the body, gives a picture of oxygen capacity.
- Leukocytes: Number of white blood cells, important for the immune system against infections.
- Platelets: Blood platelets that contribute to clotting and prevent excessive bleeding.
- HDL-cholesterol: The "good" cholesterol that protects against cardiovascular diseases by transporting excess cholesterol away from the blood vessels.
- LDL-cholesterol: The "bad" cholesterol that can form plaques in the blood vessels and increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Total cholesterol: The total amount of cholesterol in the blood, including HDL and LDL cholesterol.
- Triglycerides: Fatty substances that are stored in fat cells and affect cardiovascular health.
- Glucose: The blood sugar level that assesses the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
- HbA1c: Measurement of average blood sugar over the last 2-3 months, gives a picture of long-term blood sugar control.
- Apo A1 and Apo B: Apolipoproteins that transport cholesterol in the blood, provide a detailed picture of cardiovascular health.
- ApoB/ApoA ratio: The ratio between apolipoprotein B and A in the blood, better indicator of cardiovascular risk than traditional cholesterol measurement.