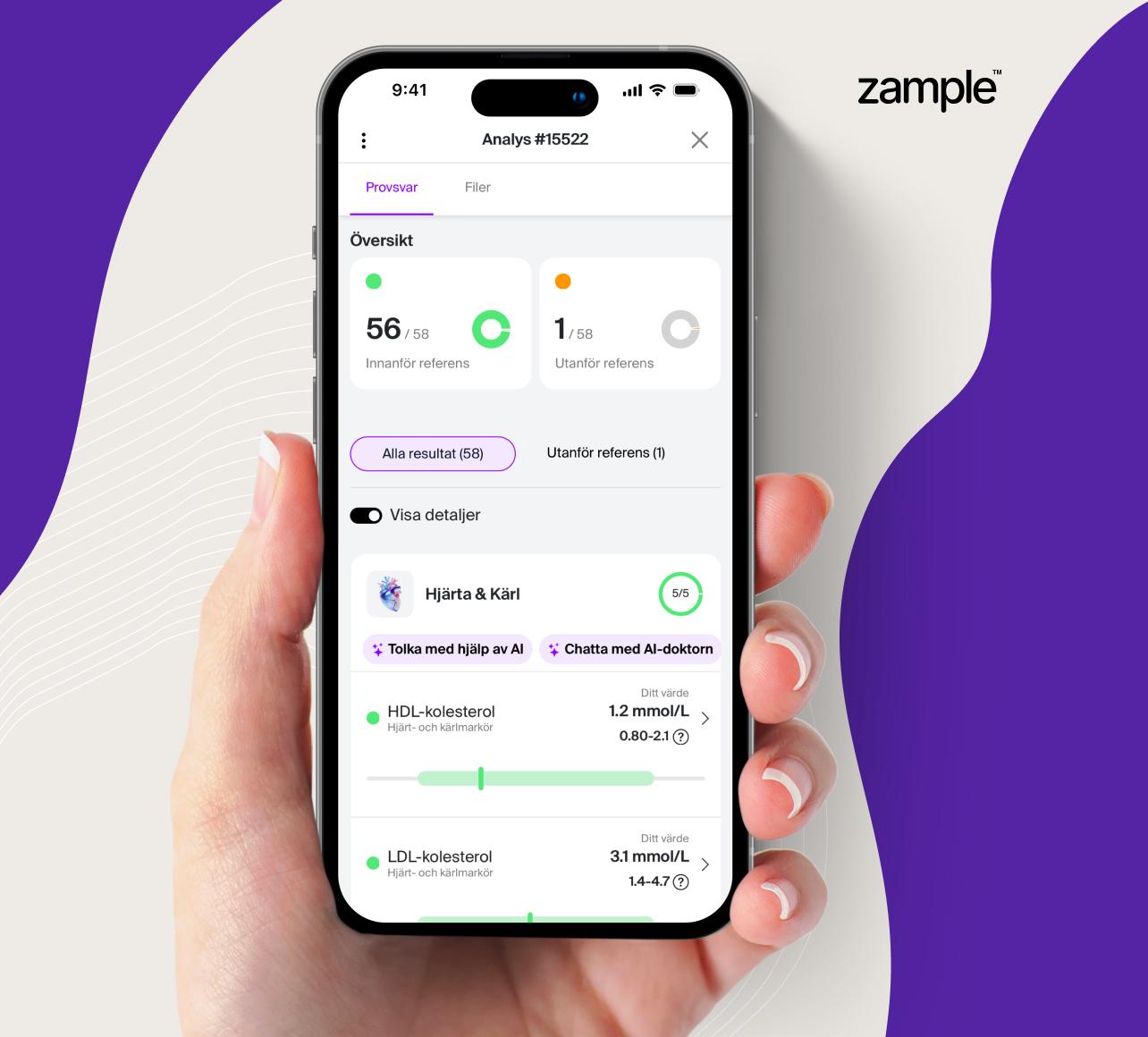
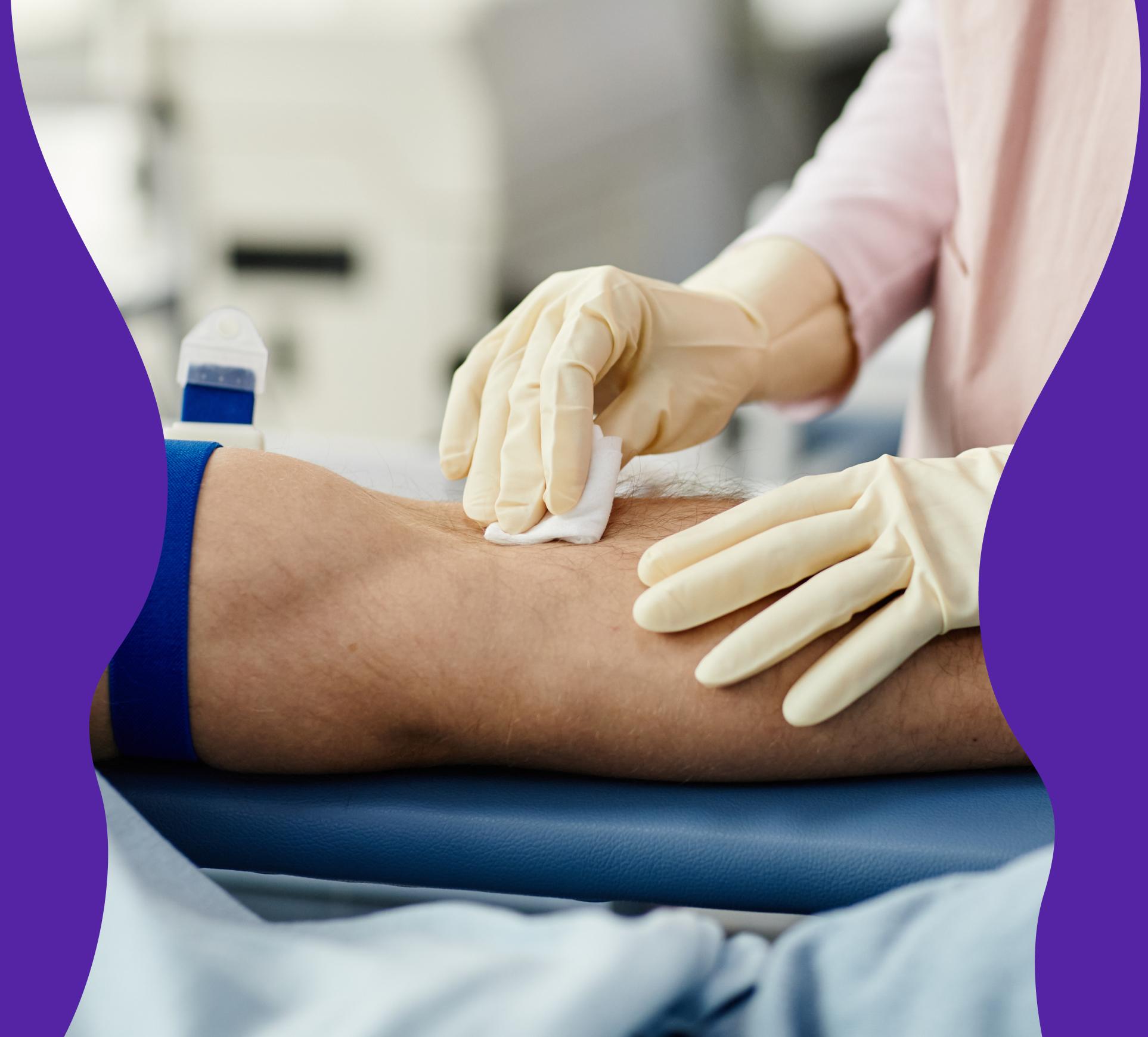
Blood test for B-Neutrophil Granulocytes – The immune system’s first line of defense against infections
Neutrophil granulocytes are the most common type of white blood cell and a central part of the body’s immune system. They are specialized in fighting bacterial infections and are part of the innate immune system. By analyzing B-Neutrophil granulocytes, you can gain a better understanding of the state of the immune system and detect any abnormalities.
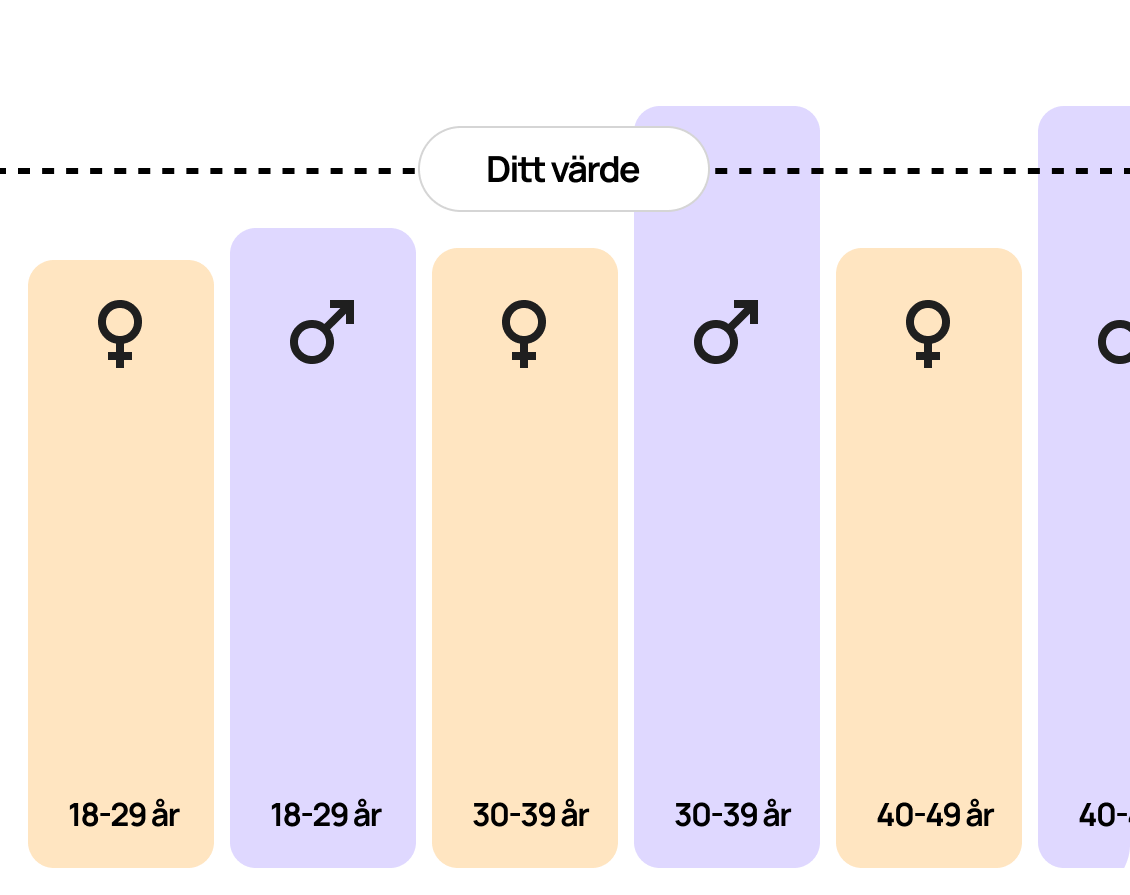
B-Neutrophil granulocytes are a type of white blood cell that quickly reacts to infections by attacking and eliminating bacteria, fungi, and other harmful microorganisms. They are produced in the bone marrow and normally make up between 40–75% of white blood cells.
High value of Neutrophil Granulocytes
Elevated levels of neutrophil granulocytes are called neutrophilia and can be a sign that the body is fighting an infection or other stress. Common causes of high neutrophil granulocytes:
- Bacterial infections
- Acute inflammation
- Physical or psychological stress
- Smoking
- Certain blood diseases, such as leukemia
- Treatment with corticosteroids
High value of Neutrophil Granulocytes
Low levels of neutrophil granulocytes are called neutropenia and can mean a weakened immune system, which increases the risk of infections. Common causes of low neutrophil granulocytes:
- Viral infections, such as influenza or HIV
- Bone marrow diseases or injuries
- Autoimmune diseases
- Effects of chemotherapy or radiotherapy
- Deficiency of vitamin B12 or folic acid
- Long-term use of certain medications
Then you should test B-Neutrophil Granulocytes
A neutrophil granulocyte analysis may be recommended in the following cases:
- Recurrent or prolonged infections
- Fever without a clear cause
- Fatigue and weakness
- Unexplained bruising or bleeding
- Suspected blood disorders or immunodeficiency