Blood test for celiac disease (gluten intolerance)
This blood test analyzes the presence of IgG antibodies against deamidated gliadin – an altered gluten protein that can provoke an immune reaction in people with celiac disease (gluten intolerance). Analysis is mainly used when celiac disease is suspected, especially if you have IgA deficiency or if results from other celiac disease tests have been unclear. It is especially recommended in cases of IgA deficiency or diffuse symptoms.
When gluten intolerance is suspected
The deamidated gliadin IgG test is recommended for people who have symptoms that may indicate celiac disease – such as prolonged stomach discomfort, fatigue, malnutrition or unexplained weight loss – but where standard tests such as transglutaminase IgA show negative results or cannot be performed due to IgA deficiency.
It is also a useful complement in the investigation of unclear immune reactions to gluten, especially in adults or in cases of atypical symptoms.
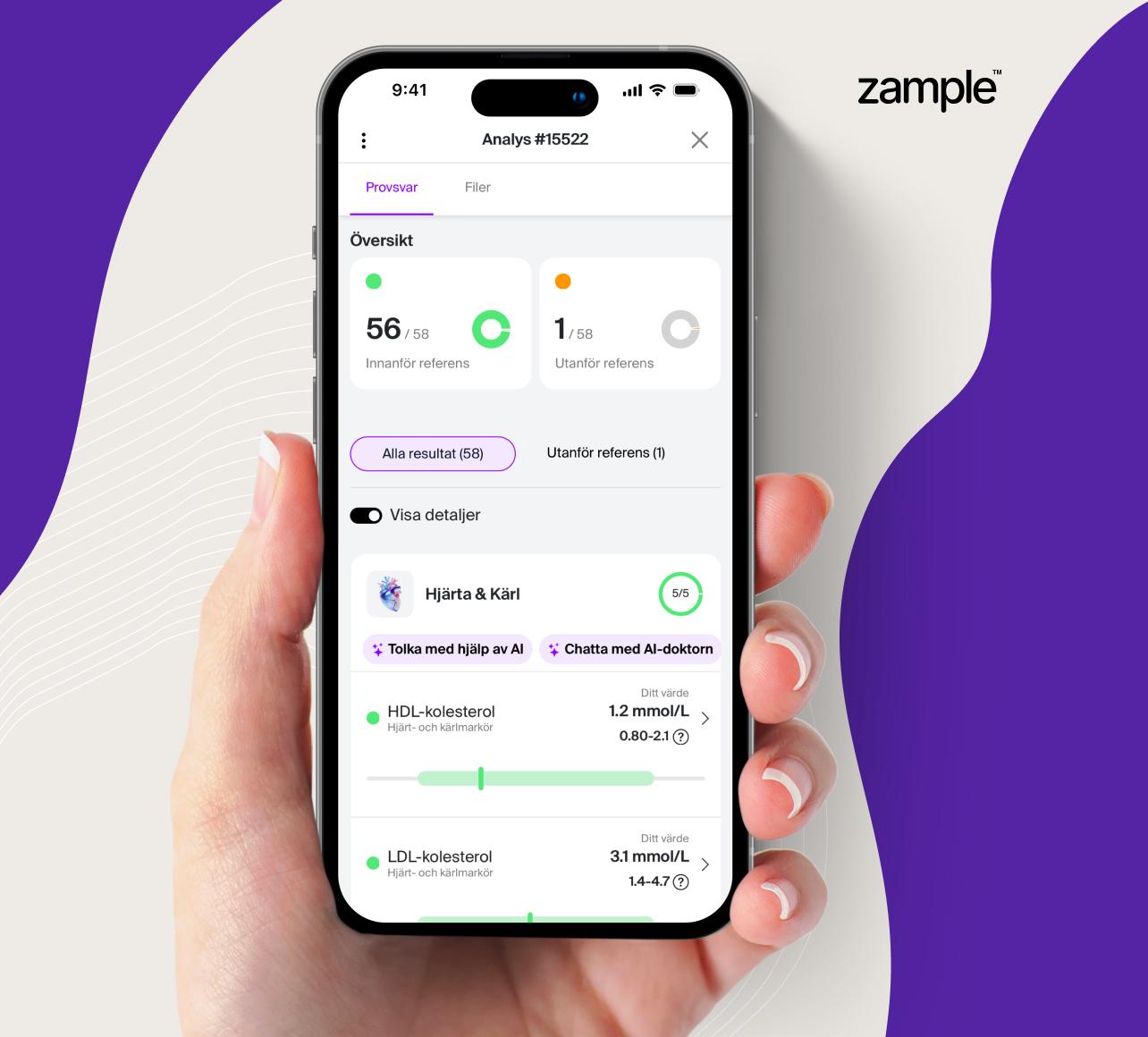
What does a Gliadin IgG test result show?
A positive result means that IgG antibodies to deamidated gliadin have been detected in the blood, which may indicate an immunological reaction to gluten. This strengthens the suspicion of celiac disease, but the test is not diagnostic in itself and should be interpreted together with other laboratory results and clinical findings.
Important information before taking the test
You should not have eliminated gluten from your diet before taking the test - the test requires that you eat gluten regularly in order to give a reliable answer. If you have already started a gluten-free diet, the result can sometimes be falsely negative.
Reference values for Deamidated gliadin IgG antibodies
- Negative: below 7 U/mL
- Limit value: 7–10 U/mL
- Positive: above 10 U/mL
Norea!Limit values may vary slightly between different laboratories. In case of limit value or positive result, further investigation is recommended.