Homocysteine is an amino acid (building block of protein) that is formed in the body during metabolism. When we eat food, it is converted into energy, during the conversion homocysteine is created. For this process to work, the body depends on sufficient amounts of both B vitamins and enzymes.
Homocysteine is therefore a natural part of the body's metabolism, but if the levels of homocysteine in the blood become elevated, it may indicate problems with the body's ability to convert and break down this amino acid. High levels of homocysteine are also associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis, stroke and heart attack. This is because an excessively high concentration of homocysteine in the blood can damage the walls of the blood vessels, which in turn can lead to inflammation and the buildup of plaque in the arteries.
In regulating homocysteine levels in the body, B vitamins play a crucial role. In particular, B12, B6 and folic acid (B9) are all necessary to convert homocysteine into other harmless substances. If the body is deficient in any of these vitamins, homocysteine can accumulate and lead to elevated levels. Therefore, a homocysteine test can be an important diagnostic tool for detecting vitamin deficiencies - mainly B12 and folate deficiencies.
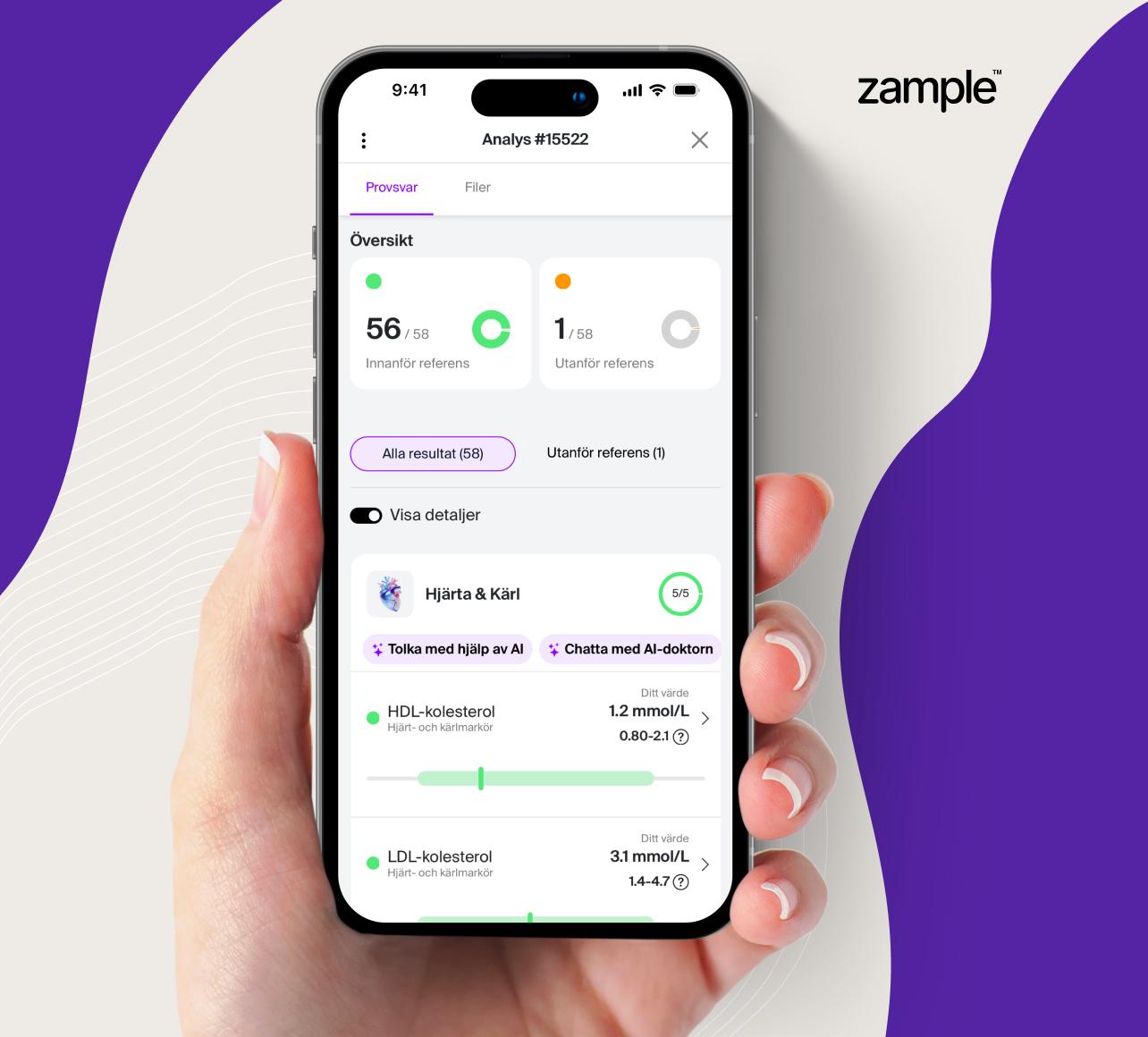
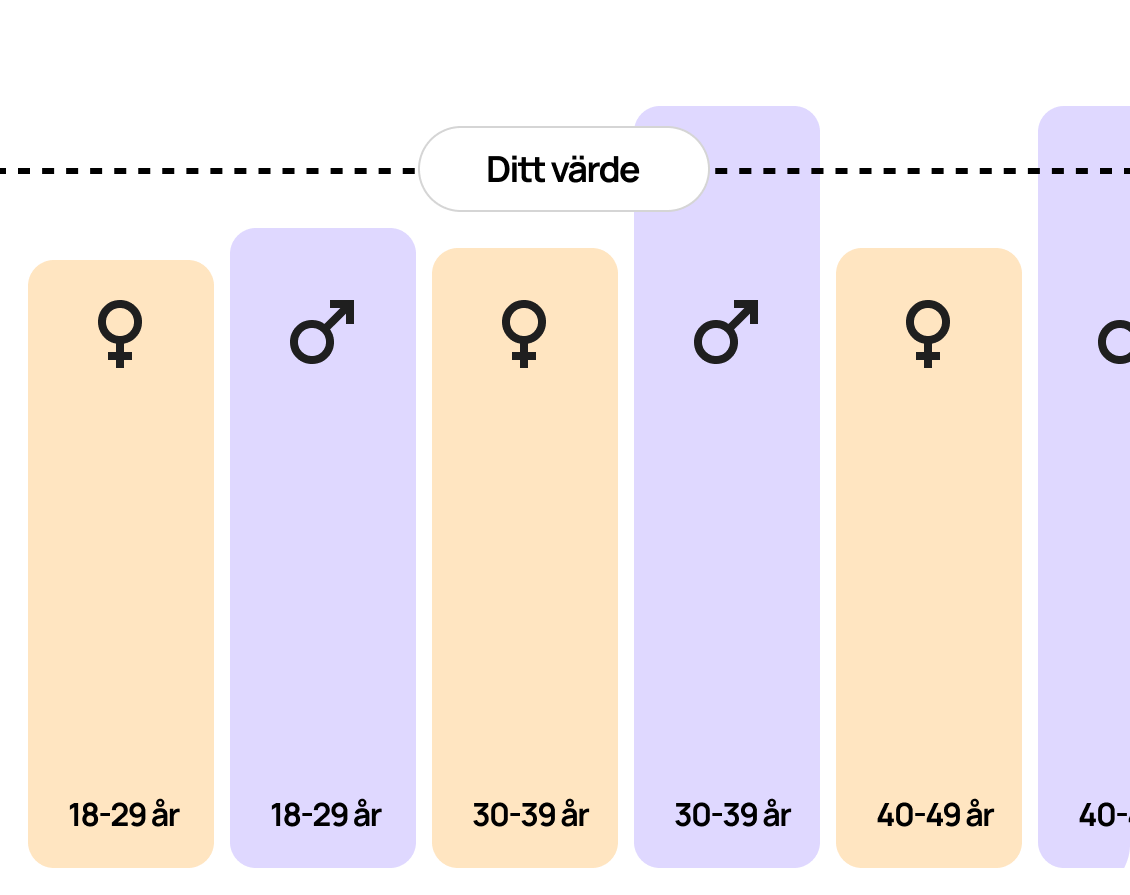
This test analyzes your homocysteine level in the body. An elevated homocysteine level is not considered serious and usually does not cause any serious problems, but it can be an indication of impaired kidney function. Homocysteine levels can be elevated due to other factors such as certain medications, various diseases or if you are deficient in vitamin B12, vitamin B6 or folate. By measuring the homocysteine level, you can detect a possible deficiency of vitamins B6, B12 and folate, as homocysteine levels rise even before the levels of vitamins B6, B12 and folate fall.
The homocysteine �blood test is not only used to assess the risk of cardiovascular disease, but also to monitor patients with diagnosed conditions that affect vitamin status, such as malabsorption or genetic mutations (MTHFR gene mutation) that can interfere with the body's ability to process folic acid. The blood test may also be relevant in the investigation of dementia or cognitive disorders, as high homocysteine levels have been shown to be linked to impaired cognitive function.
What can elevated homocysteine levels indicate?
If your homocysteine levels are elevated, treatment may include supplementation with B vitamins and possible lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications. Eating a balanced diet with enough B-vitamin-rich foods such as green leafy vegetables, meat, fish, and dairy products can also help keep homocysteine levels within the normal range.