Apolipoprotein A1 (Apo A1) – A Key Marker for Heart Health
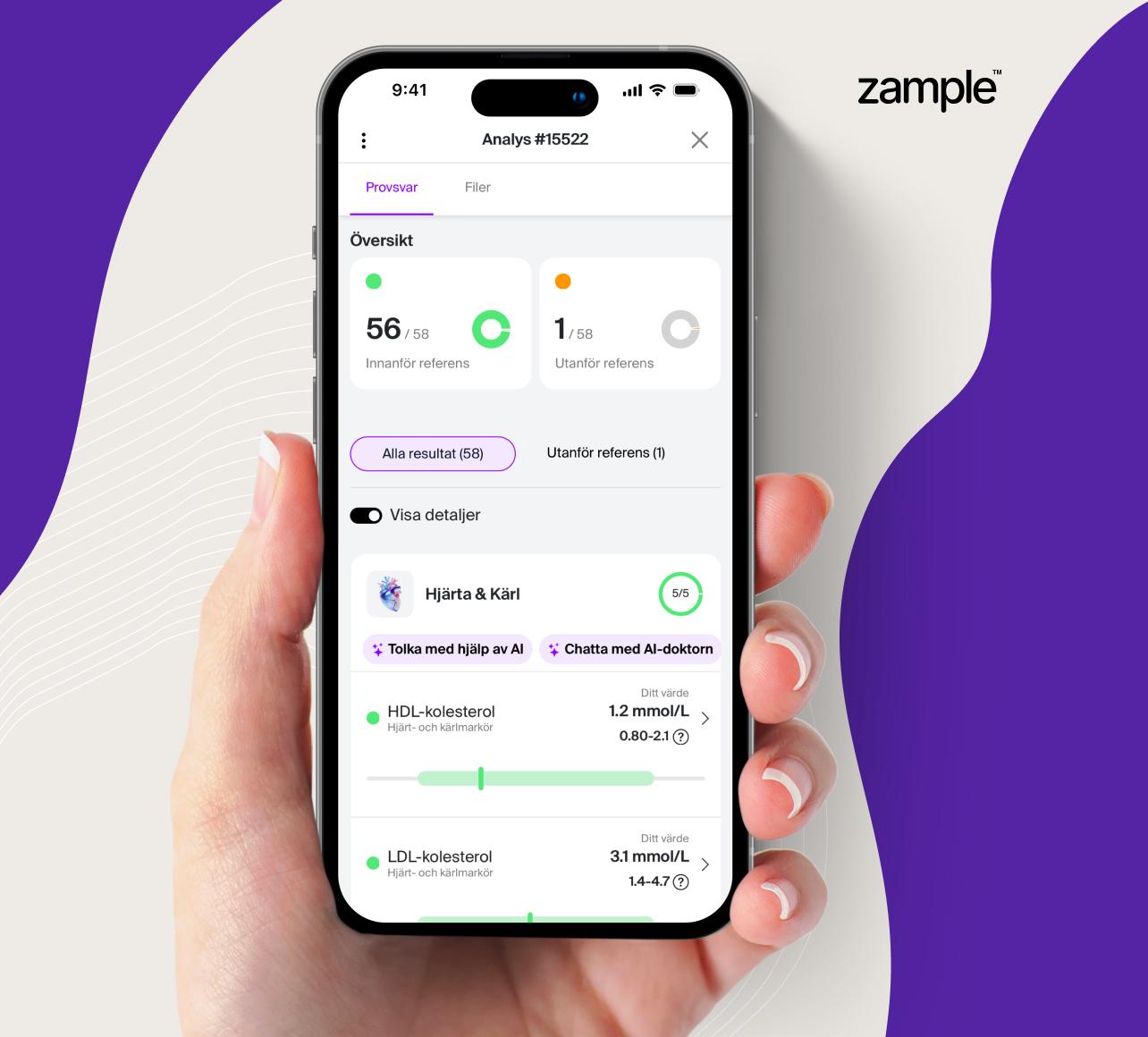
Apolipoprotein A1 is the main protein component of high-density lipoprotein (HDL cholesterol), also known as the “good cholesterol.” Its primary function is to transport excess cholesterol from tissues and blood vessels back to the liver, where it can be broken down and excreted. This process is crucial for preventing the buildup of plaque in blood vessels, thereby reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
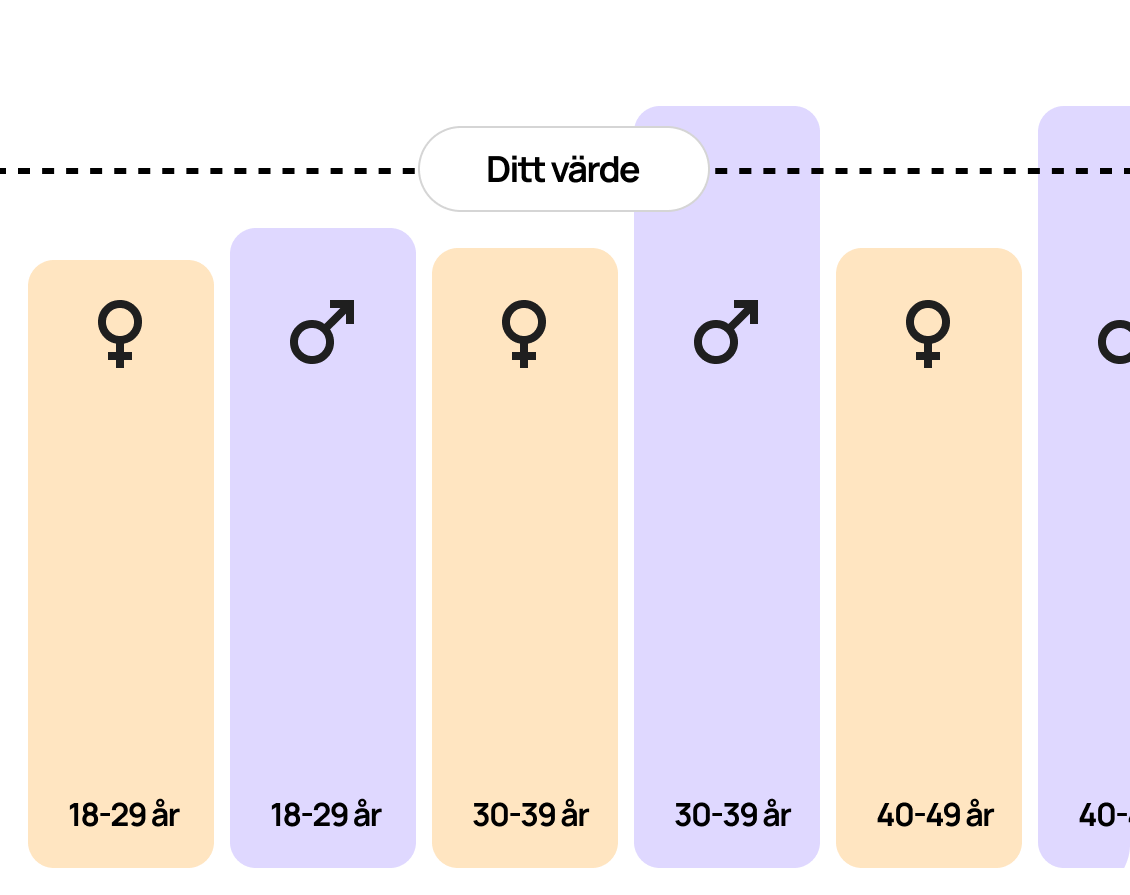
Research has shown that high levels of Apo A1 are associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease, while low levels may be an indication of increased cardiovascular risk. Apolipoprotein A1 is therefore an important biomarker for assessing lipid metabolism and heart health more precisely than traditional cholesterol tests.
Cardiovascular disease can often be prevented by making lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in unsaturated fats and fiber, and quitting smoking. If necessary, drug treatment for high blood pressure and elevated blood lipids can also be an important part of risk reduction.
Why measure Apolipoprotein A1?
The Apo A1 test is primarily used to:
- Assess cardiovascular risk more accurately than traditional HDL measurements.
- Evaluate lipid metabolism in people with suspected or known dyslipidemia.
- Identify patients with an increased risk of atherosclerosis, especially those with diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
- Monitor the effect of treatment for high blood lipids, such as statins or other lipid-modulating drugs.
Low levels of Apo A1 may be a signal that HDL function is impaired, which means an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Low values can be caused by, for example, smoking, inflammation, insulin resistance, kidney disease or genetic factors.
Apolipoprotein A1 and Apo B – A more detailed picture of blood lipids
For a more comprehensive picture of blood lipid status and cardiovascular risk, it is recommended that Apo A1 is measured in combination with Apolipoprotein B (Apo B). While Apo A1 reflects the protective function of HDL cholesterol, Apo B represents the cholesterol particles (LDL and other atherogenic lipoproteins) that can contribute to plaque formation in the blood vessels.
By analyzing both of these biomarkers, you gain a deeper understanding of your heart health and the opportunity to take the right measures to optimize your blood lipid profile. We therefore recommend that you also order an analysis of Apolipoprotein B (Apo B) in connection with the Apo A1 sample.