Blood test for B-Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that play a crucial role in the body's immune system. They are part of the adaptive immune response, helping to protect the body against viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens. Lymphocytes are produced in the bone marrow and circulate in the blood, lymphatic system, and tissues, where they contribute to the immune defense.
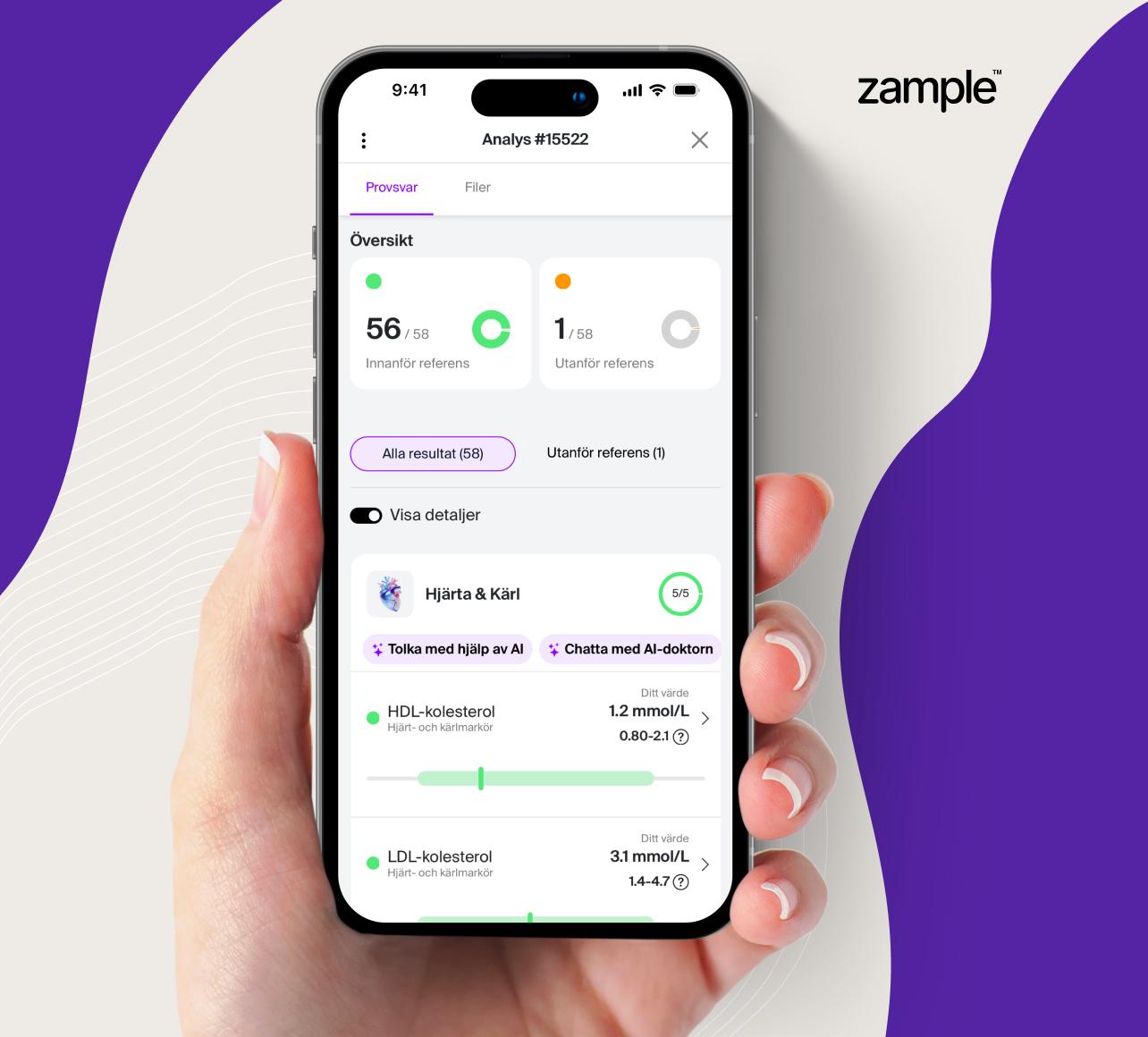
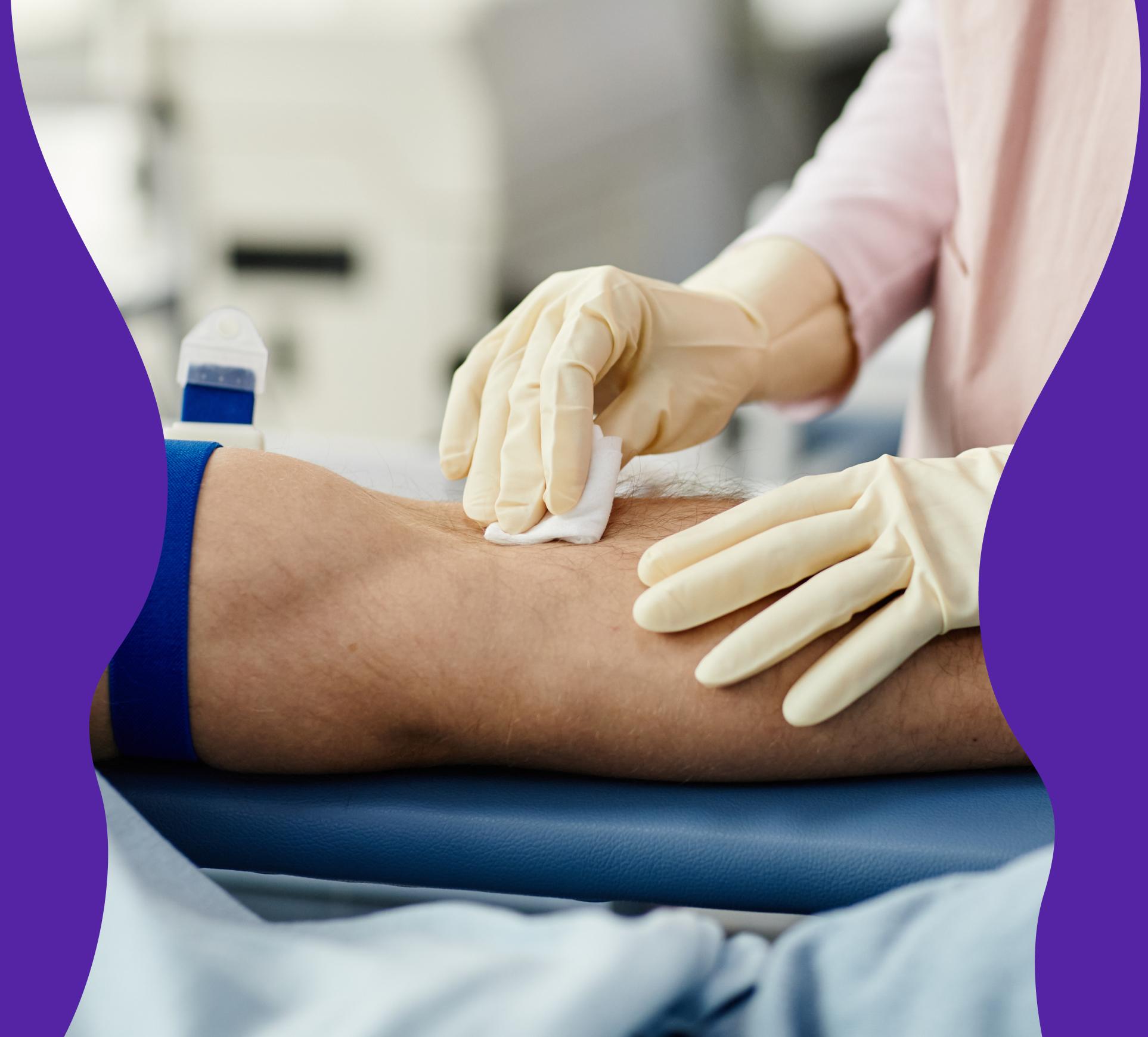
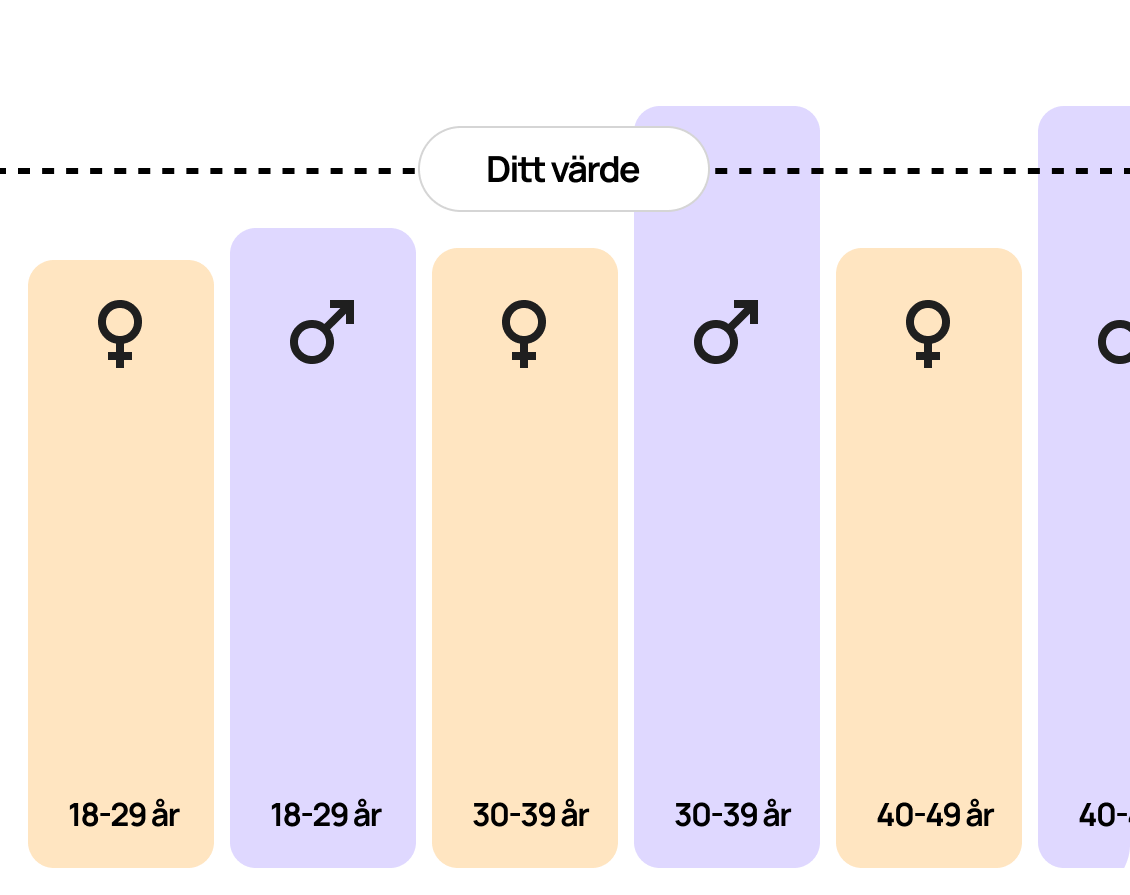
A blood test for B-Lymphocytes is used to measure the number of lymphocytes in the blood. Abnormal lymphocyte levels may indicate infections, autoimmune diseases, inflammation, or blood disorders. This test is often included as part of a broader blood analysis to assess immune function and overall health status.
Analysis of immune cells
The B-Lymphocyte blood test is used to determine whether lymphocyte levels in the blood are within the normal range or if there are signs of infection, inflammation, or immune-related diseases. This test can be an important part of the diagnostic process when evaluating suspected immunodeficiency, chronic infections, or autoimmune disorders.
What does a high lymphocyte count indicate?
Elevated lymphocyte levels, known as lymphocytosis, may indicate that the body is responding to an infection or another immune stimulus.
Common causes of high lymphocyte levels:
- Viral infections such as influenza, mononucleosis (glandular fever), or hepatitis
- Chronic infections such as tuberculosis
- Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or multiple sclerosis
- Chronic inflammation
- Cancers such as leukemia or lymphoma
High lymphocyte levels can be part of the body's normal immune response to infections but may require further investigation if significantly elevated or persistently high over time.
What does a low lymphocyte count Indicate?
Low lymphocyte levels, known as lymphocytopenia, may indicate a weakened immune system, which can increase the risk of infections.
Common causes of low lymphocyte levels:
- Viral infections such as HIV or measles
- Autoimmune diseases affecting the immune system
- Chronic diseases such as kidney failure or liver disease
- Effects of chemotherapy or radiation therapy
- Long-term use of corticosteroids
- Bone marrow disorders that impair blood cell production
When lymphocyte levels are low, further investigation may be necessary to determine the cause and, if needed, follow up with additional tests.
When Is a B-Lymphocyte test recommended?
A lymphocyte test may be relevant if you experience symptoms such as:
- Recurrent or prolonged infections
- Persistent fatigue and weakness
- Fever without a clear cause
- Unexplained bruising or bleeding
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Unexplained weight loss
If you have symptoms suggesting impaired immune function or a chronic infection, a blood test for lymphocytes can provide valuable information about your health.