B-Platelet Count (BPC) Blood Test – Coagulation Ability Analysis
Platelets, also known as platelets or BPC, are a type of blood cell that helps the blood clot. Platelet counts are often ordered as part of a routine blood test or as part of a medical evaluation for a variety of reasons, including to help diagnose bleeding or clotting disorders or to monitor treatment for these conditions.
They help stop bleeding by forming a clot when blood vessels are damaged. A B-Platelet Count (BPC) blood test measures the amount of platelets in the blood and can provide important information about the body's ability to control bleeding and heal wounds.
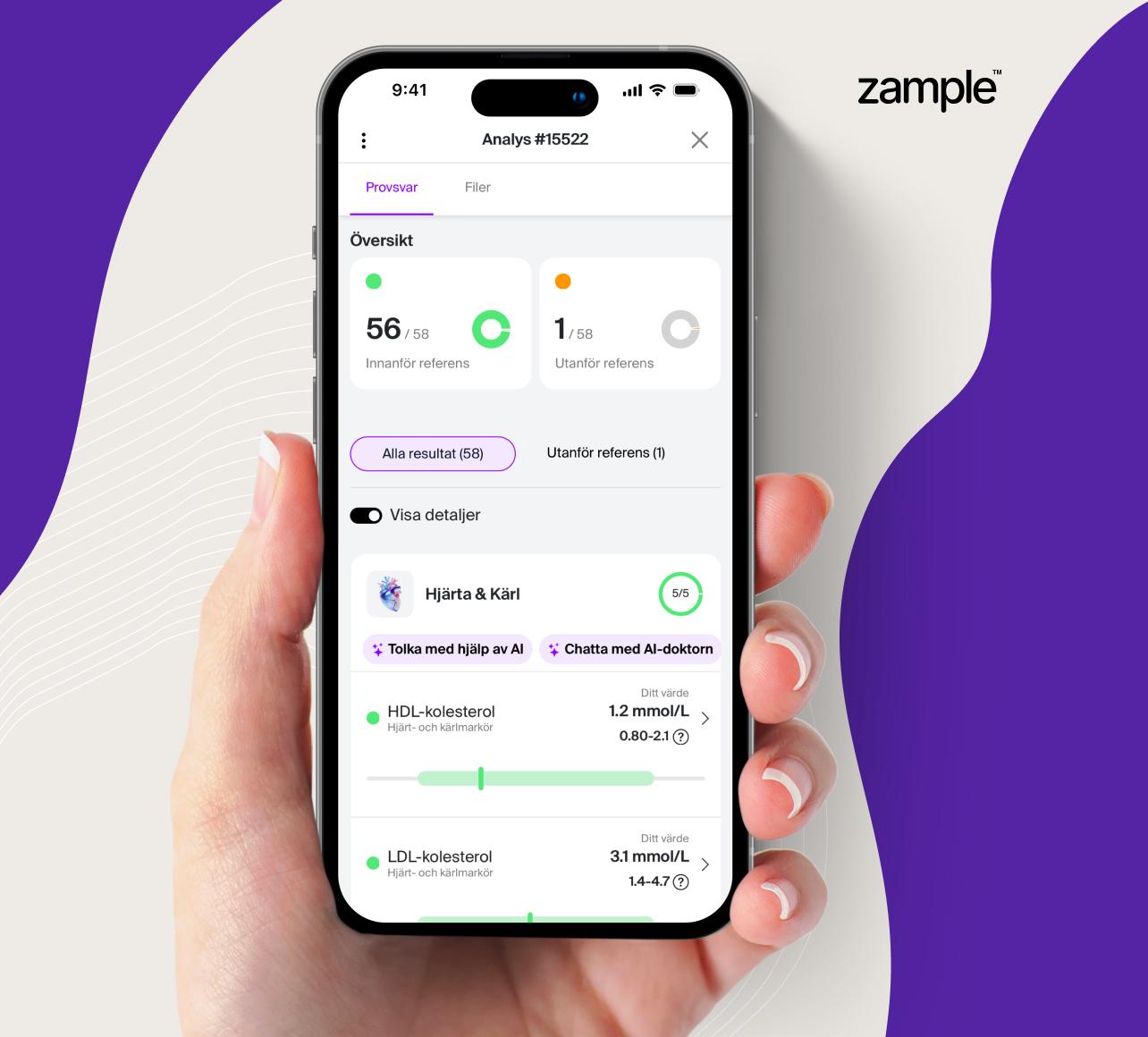
The BPC test is often used to evaluate bleeding tendencies, clotting disorders, and suspected diseases that affect the composition of the blood. It is also part of a complete blood count to provide an overall picture of blood health.
What are B-Platelets and why is it important to analyze them
B-Platelets (TPK) are an important part of the body's hemostasis, the system that regulates the blood's ability to clot. When blood vessels are damaged, platelets are activated and clump together to quickly form a blood clot, preventing further blood loss.
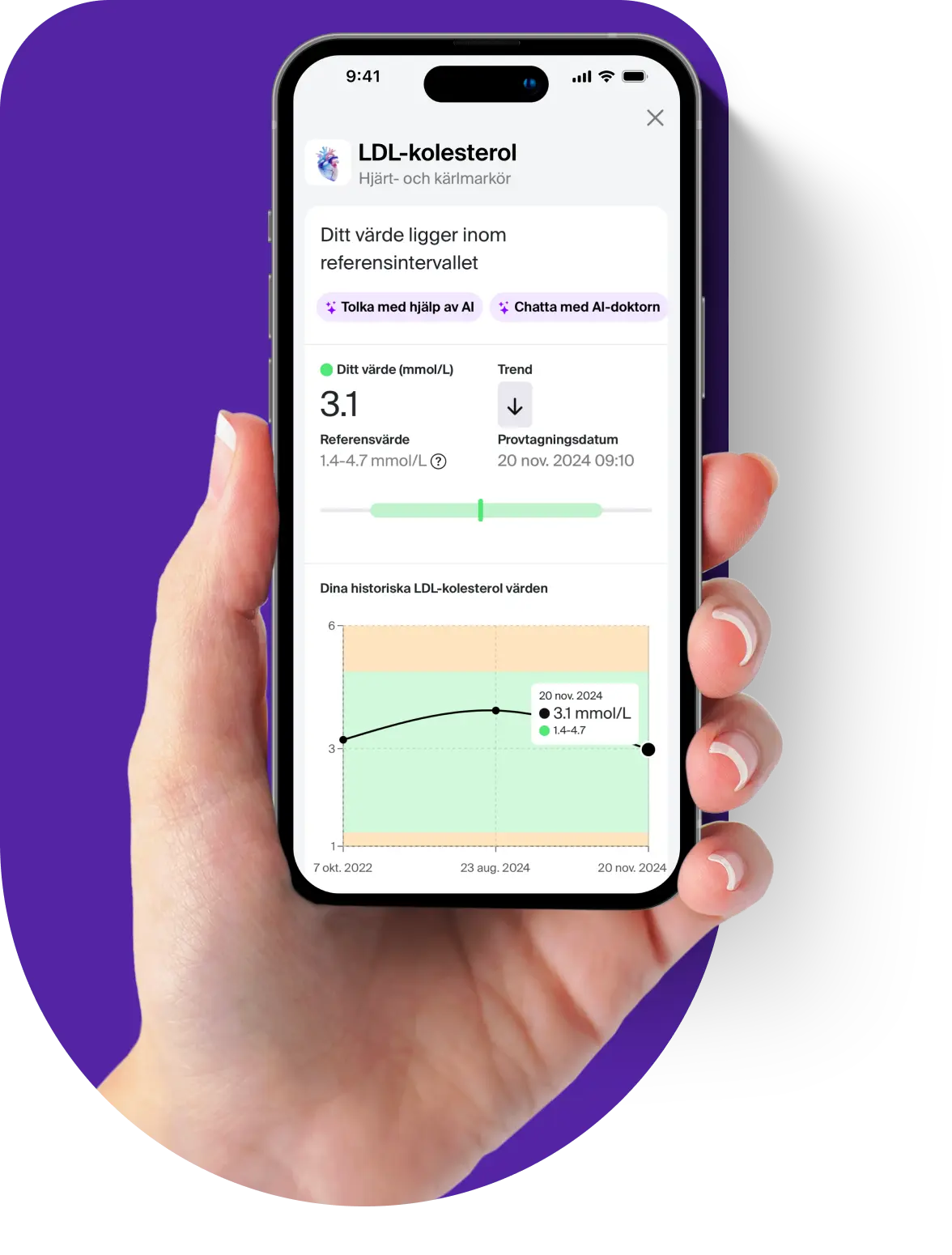
Normal platelet values are usually between 150–350 x10⁹/L, but this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory's reference range. Abnormal values can indicate different disease states and should be assessed together with other blood markers.
B-Platelet high value
An elevated platelet count is called thrombocytosis and can be a reaction to an ongoing process in the body or a sign of an underlying disease.
Common causes of high platelets:
- Inflammatory diseases
- Infections
- Iron deficiency
- Chronic diseases
- Polycythemia vera or essential thrombocythemia (blood diseases)
- Recovery after surgery or major blood loss
If B-Platelet is elevated, it can in some cases mean an increased risk of blood clots and should be investigated further if values are persistently high.
B-Platelet low value
A low platelet count is called thrombocytopenia and can lead to increased bleeding and is caused by;
- Viral infections such as hepatitis or HIV
- Bone marrow diseases
- Autoimmune diseases such as ITP (Immunological thrombocytopenia)
- Liver or kidney disease
- Side effects of certain medications, such as chemotherapy
- Vitamin B12 or folic acid deficiency
If platelet levels are low, it can lead to an increased risk of bruising, prolonged bleeding and spontaneous nosebleeds.
When should you test your B-Platelets?A TPK analysis may be relevant for symptoms such as:
- Bruising that occurs easily
- Prolonged or spontaneous bleeding
- Nosebleeds or bleeding gums
- Signs of blood clot formation such as swelling or pain in the leg
- Headache and dizziness with elevated values
- Monitoring for blood diseases or ongoing treatment
The test is for those who want to gain insight into your TPK value. Along with several other markers for red and white blood cells, TPK (Platelet Count) is also included in the blood status and b-cell test.