Analysis of Cancer Antigen S- CA 125
A blood test to measure the concentration of CA 125, a tumor marker primarily used to identify or monitor ovarian cancer. By analyzing CA 125 levels, doctors can obtain important information about the presence and progression of ovarian cancer as well as how well ongoing treatment is working. Elevated levels can also be seen in other cancers and benign conditions, making the test valuable in various clinical contexts.
Uses of the CA 125 Test
The CA 125 test is used in several clinical situations where it is important to assess the presence or treatment of cancer, primarily ovarian cancer. Common situations where the test is recommended include:
- Suspected ovarian cancer
- Monitoring treatment for ovarian cancer
- Detecting ovarian cancer recurrence
When is a CA 125 Test Recommended?
The analysis of CA 125 is recommended when there is suspicion of ovarian cancer or other gynecological cancers. The test is also used to monitor patients who are already being treated for cancer, to assess treatment effectiveness and detect potential recurrences. CA 125 levels can be elevated in other cancers, such as endometrial cancer, pancreatic cancer, and lung cancer, as well as in certain non-cancerous conditions like endometriosis, liver cirrhosis, and inflammatory diseases.
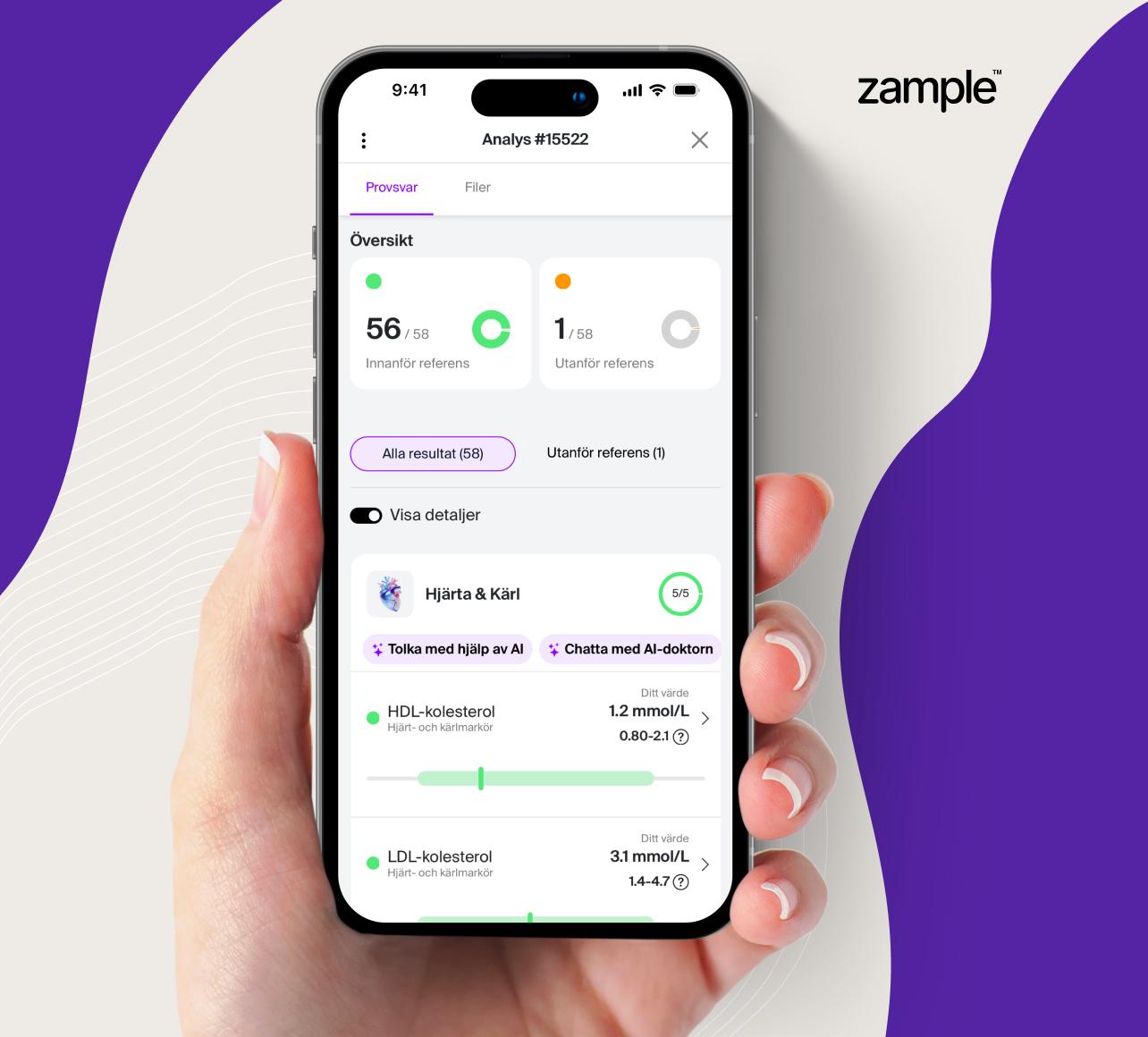
Reference Range for CA 125
Normal reference values for CA 125 are usually below 35 kU/L. Levels above this may indicate the presence of ovarian cancer or other diseases. It is important to note that reference values may vary depending on the laboratory and the method used for CA 125 analysis, and normal variations exist, so results should be interpreted with caution.
Interpretation of CA 125 Test Results
Normal CA 125 levels are usually below 35 kU/L. Elevated CA 125 levels may indicate ovarian cancer or other malignancies such as endometrial cancer, pancreatic cancer, or breast cancer. Elevated levels can also be seen in benign conditions like endometriosis or inflammatory diseases. To obtain a complete picture, the results should be interpreted alongside other examinations, such as imaging and clinical findings.