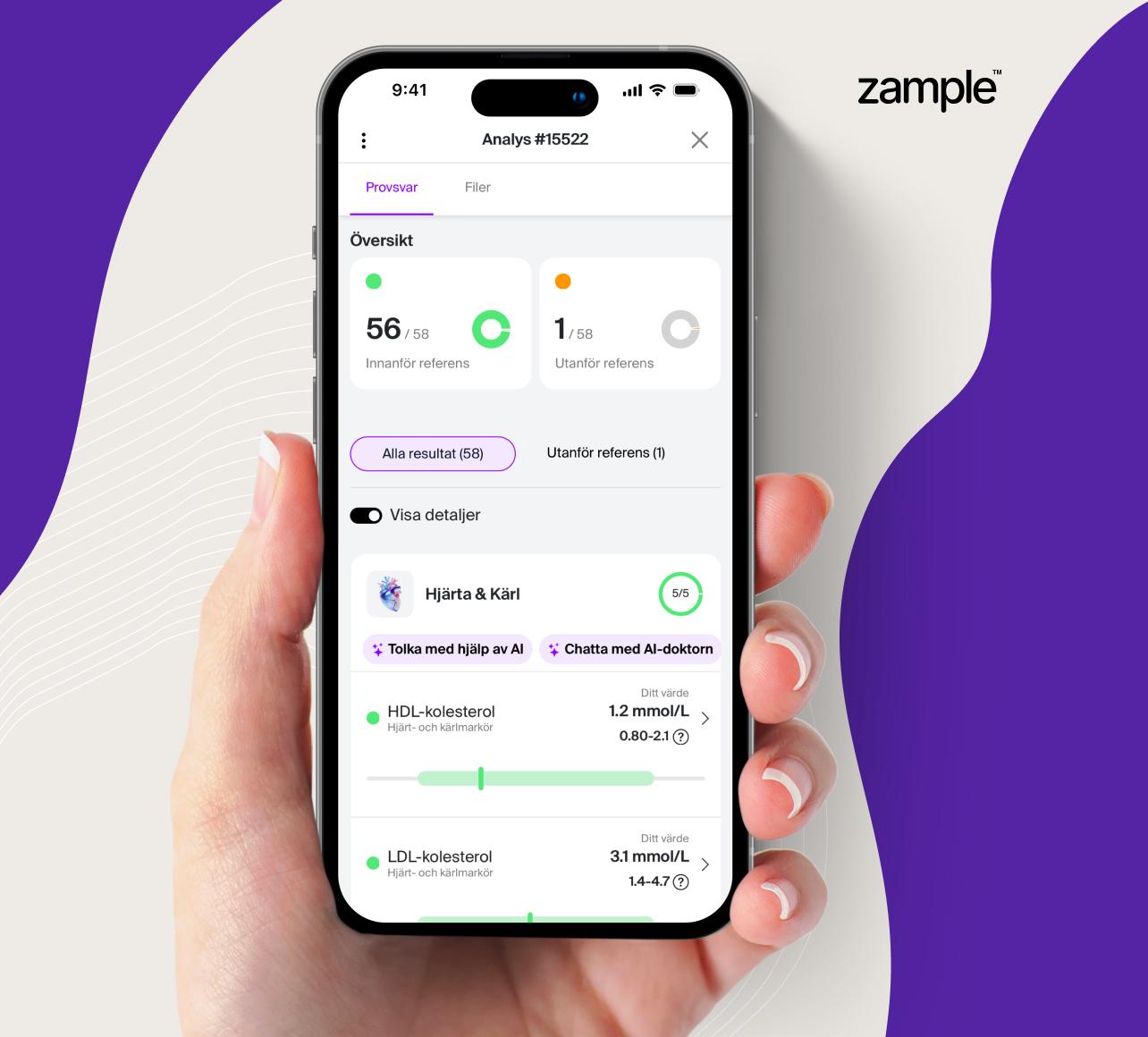
Infection test - Immunoglobulin M
Blood analysis of Immunoglobulin M (IgM), which is a central part of your primary immune system. The test helps identify and monitor immune-related conditions and infections that may affect your health.
Why should you do an IgM test?
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is the first antibody produced by the immune system in response to an infection. Measuring the levels of IgM in the blood can provide important information about the activity of your immune system and help identify ongoing or recent infections. You should consider having this test if you experience the following symptoms or suspicions:
- Unclear infections: If acute infections are suspected, such as influenza, hepatitis or Epstein-Barr virus, an IgM test can help confirm the diagnosis.
- Recurrent infections: If you have frequent or difficult-to-treat infections, an IgM test can provide insight into possible immunodeficiency conditions.
- Autoimmune diseases: If autoimmune diseases are suspected, where the immune system attacks the body's own tissues, the IgM levels can provide valuable information.
- Treatment monitoring: If you are being treated for an infection or immune-related condition, an IgM test may be used to monitor treatment effectiveness.
- Autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, where the immune system attacks healthy tissues
- Bacterial or viral infections
- Cancer such as leukemia and lymphoma
- Allergic reactions
Low IgM values are related to:
- Diseases of the immune system, such as HIV/AIDS
- Primary immunodeficiency diseases, such as X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA)
- Diseases of the liver or spleen
When is the Immunoglobulin M (IgM) test recommended?
- Individuals who desire a comprehensive evaluation of their immune system status.
- People with symptoms of infection or inflammation who want a clearer diagnosis.
- Those who follow up existing health conditions or treat specific diseases related to the immune system.
- Health conscious individuals who want regular updates on their health.