Leukocytes – White Blood Cells
Leukocytes, or white blood cells, are a crucial part of the body's immune system. They act as the body's "defense soldiers" and protect against infections, fight foreign substances, and help keep you healthy. Measuring the number of leukocytes in your blood can provide important information about your body's ability to fight infections, inflammation, and other health problems.What can a leukocyte blood test show?
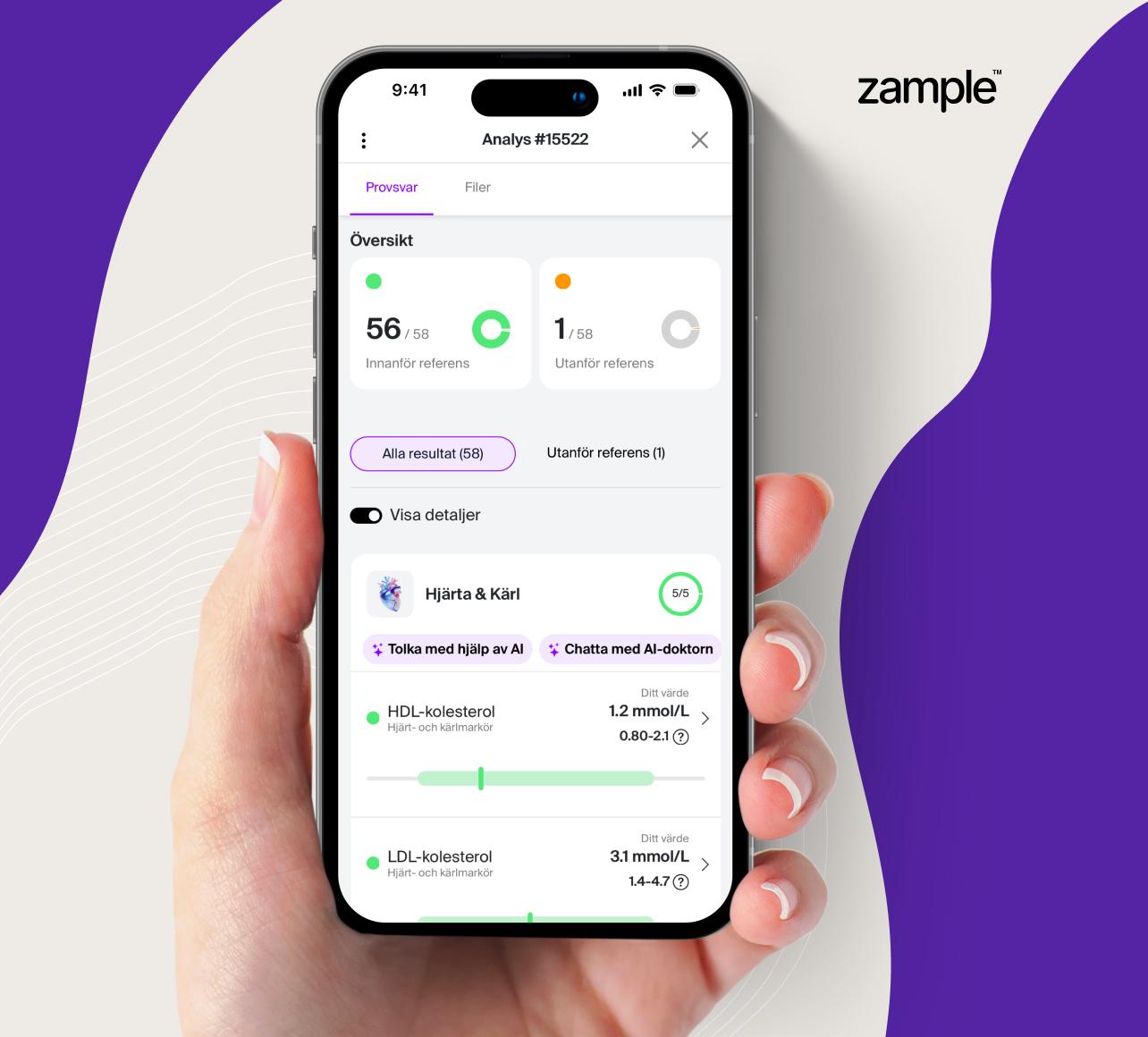
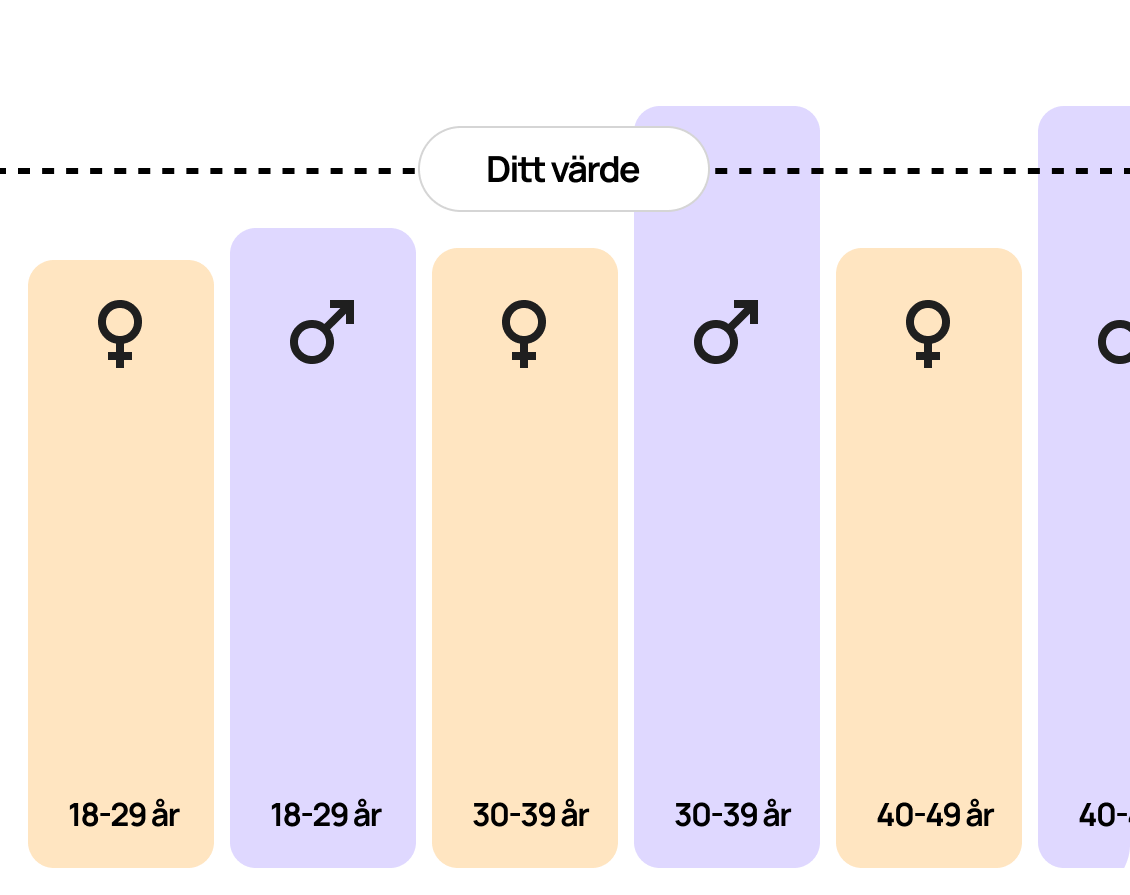
A leukocyte test measures the amount of white blood cells in your blood (WBC, leukocyte particle concentration). Deviations from the normal count can indicate several different health conditions:
Elevated leukocyte counts (leukocytosis)
Can be caused by infections, inflammation, stress, certain medications, or more serious conditions such as blood disorders.
Low counts (leukopenia)
Can signal viral infections, drug interactions, autoimmune diseases, or problems with the bone marrow where leukocytes are produced.
When should you test your leukocytes?
A leukocyte count test may be necessary if you experience symptoms such as recurrent infections, fever without a clear cause, persistent fatigue, unexplained bruising or bleeding that does not go away, or swollen lymph nodes. These symptoms may indicate that your immune system is affected or that an underlying disease needs to be investigated.
Leukocytes are usually analyzed as part of a larger blood count, which gives you a broader picture of the composition of your blood, including red blood cells and platelets. This can be useful in evaluating your overall health or detecting early signs of illness before symptoms become apparent.