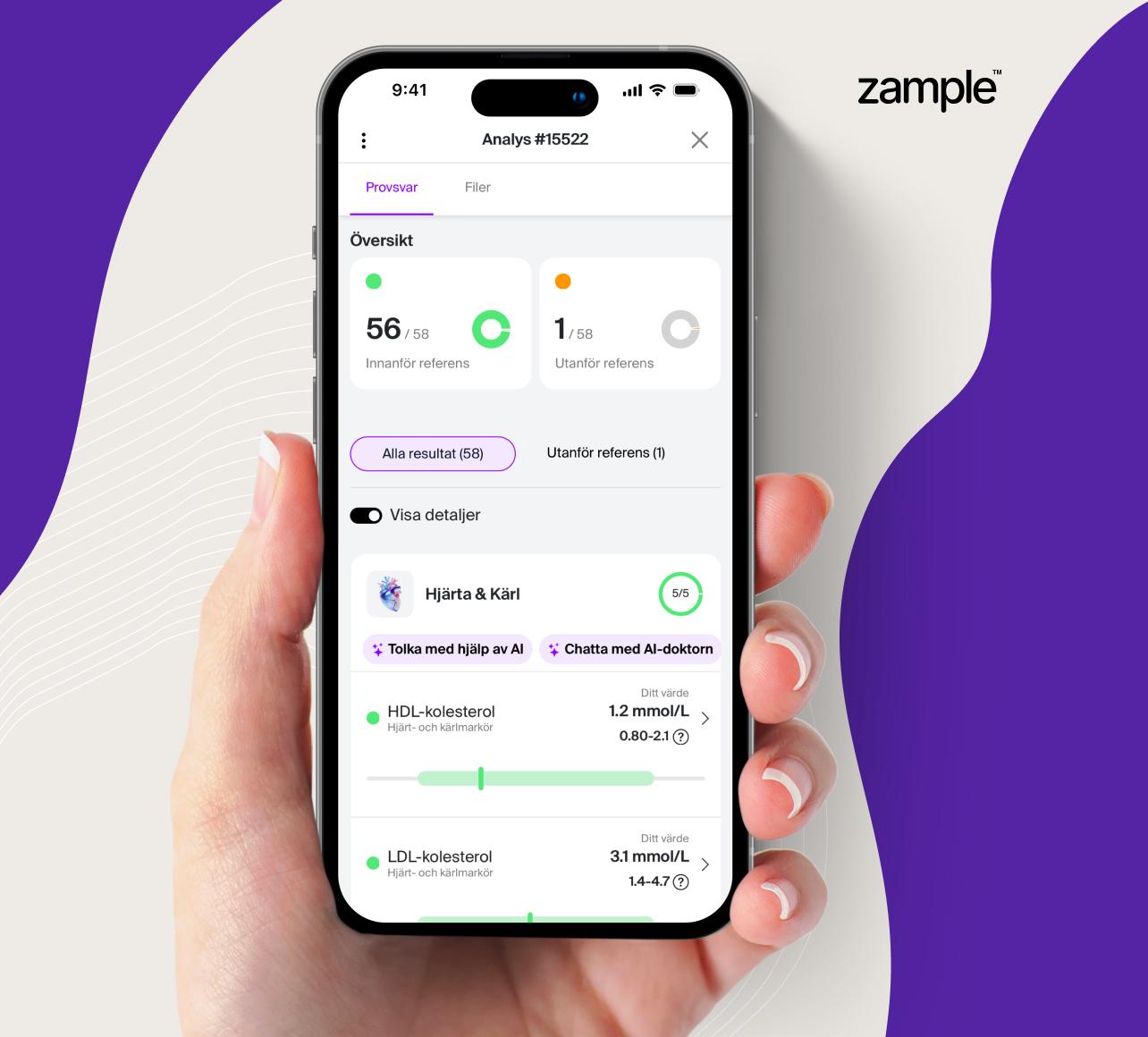
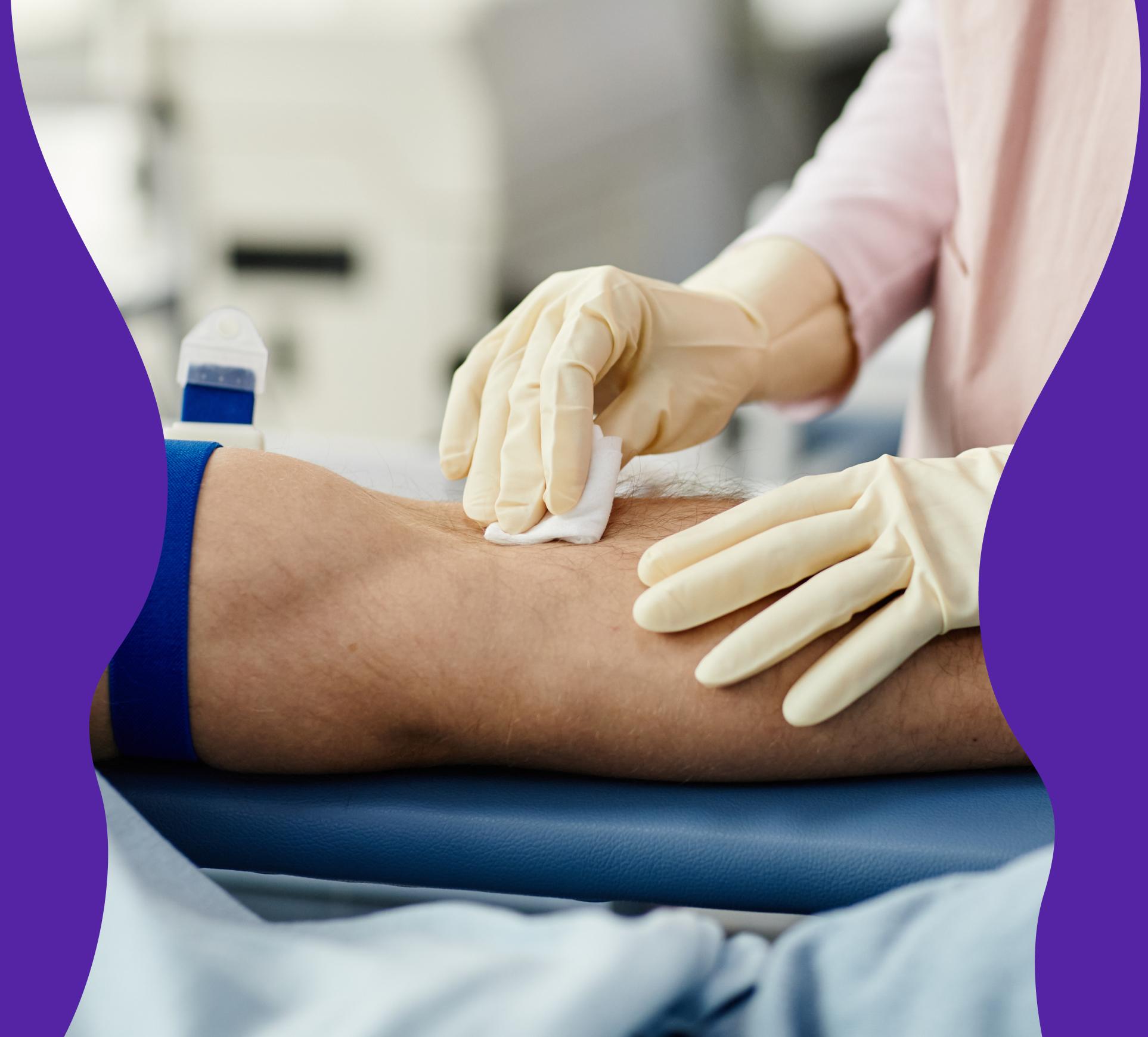
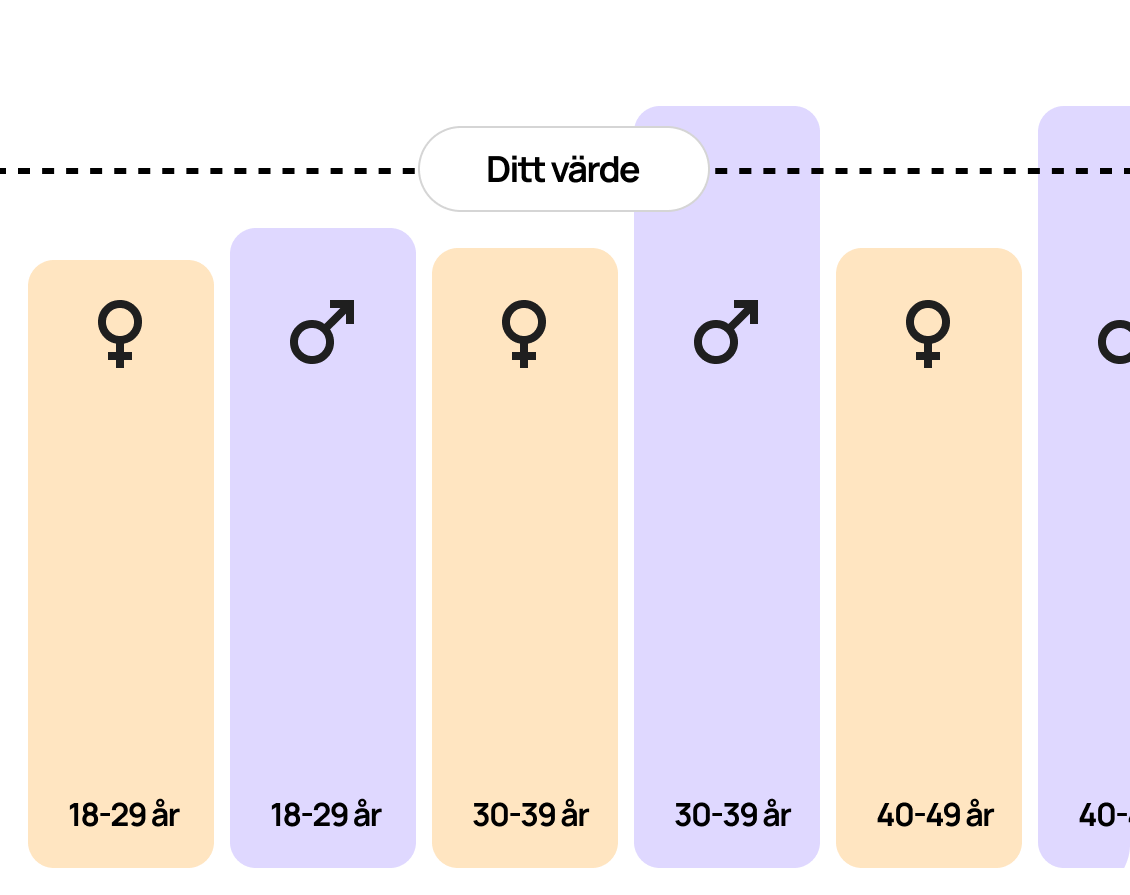
Blood test for B-Hemoglobin (Hb)
Hemoglobin (Hb) is an iron-containing protein found in red blood cells. Its primary function is to transport oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and to return carbon dioxide to the lungs for exhalation. Hemoglobin gives blood its red color and plays a crucial role in the body's respiratory function by ensuring oxygen delivery to cells and organs.
Measuring hemoglobin levels in the blood provides important information about the blood's oxygen transport capacity and can help identify various health conditions. Both low and high levels of hemoglobin can cause symptoms and may indicate underlying medical conditions.
Why test B-Hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin measurement is a key component of a complete blood count (CBC) and is used to assess blood oxygen transport capacity, detect deficiencies, and identify imbalances in blood cell production. The Hb blood test may be relevant in cases of:
- Suspected anemia – Low hemoglobin levels may indicate iron deficiency, blood loss, or deficiencies in vitamins such as B12 and folic acid.
- Evaluation of chronic diseases – Conditions such as kidney disease, inflammatory diseases, or cancer can affect hemoglobin levels.
- Assessment of oxygen transport capacity – Athletes, individuals living at high altitudes, or those with heart and lung diseases may need to monitor their hemoglobin levels.
- Monitoring dehydration – High hemoglobin levels may indicate fluid deficiency.
Low Hemoglobin (Hb) – What does it mean?
A low hemoglobin level may indicate anemia, meaning the body has too few red blood cells or that they are not functioning properly. This can lead to oxygen deficiency in the body's tissues.
Common causes of low hemoglobin:
- Iron deficiency (the most common cause of anemia)
- Vitamin B12 or folic acid deficiency
- Chronic diseases such as kidney failure or inflammatory conditions
- Blood loss, such as from gastrointestinal bleeding or heavy menstruation
- Bone marrow disorders affecting blood cell production
Symptoms of low hemoglobin
- Fatigue and weakness
- Pale skin and mucous membranes
- Dizziness and headaches
- Shortness of breath and heart palpitations during exertion
- Cold hands and feet
High Hemoglobin (Hb) – What does it mean?
Elevated hemoglobin levels can occur in various conditions and may indicate that the body is compensating for reduced oxygen transport or dehydration.
Common causes of high hemoglobin:
- Dehydration
- Smoking or lung diseases such as COPD
- Chronic heart and lung diseases
- Polycythemia vera (a blood disorder causing an overproduction of red blood cells)
Symptoms of High Hemoglobin:
- Headaches and dizziness
- Facial flushing
- Increased risk of blood clot formation and cardiovascular disease
- Poor circulation in hands and feet
The B-Hemoglobin (Hb) blood test is an important analysis for assessing the blood's oxygen transport capacity and can provide valuable insights into overall health. Low levels may indicate anemia, while high levels can signal dehydration or underlying conditions.
Since hemoglobin is a key component of a complete blood count, it is often analyzed alongside other blood tests to provide a more comprehensive picture of blood cell production and oxygenation status.