Quick version
The cervical spine is central to head movements and nerve function, but sensitive to strain and injury.
- Consists of seven cervical vertebrae (C1–C7)
- Enables head movements and protects the spinal cord
- Common complaints are pain, stiffness and nerve damage
- Can be affected by herniated discs, osteoarthritis and whiplash
- Investigated using clinical and imaging methods
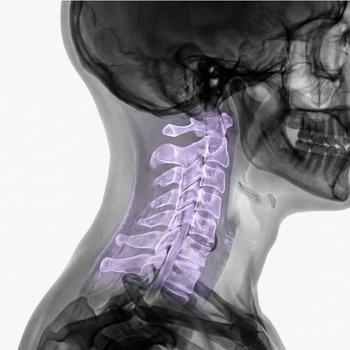
What is the cervical spine?
The cervical spine consists of the seven uppermost vertebrae in the spine, designated C1–C7. The cervical spine connects the skull to the thoracic spine and enables movements such as flexion, rotation, and extension of the neck. The cervical spine surrounds and protects the upper part of the spinal cord.
Anatomy and structure
The seven cervical vertebrae, C1-C7, are smaller than the lower vertebrae but are very mobile. The two uppermost, atlas (C1) and axis (C2), allow for a great deal of freedom of movement in the head. Between the vertebrae are discs that act as shock absorbers.
Function and mobility
The cervical spine provides support for the head and enables movements such as twisting, bending, and bending backward. It also plays an important role in balance and eye coordination through interaction with the central nervous system.
Nervous system and blood vessels
The spinal cord passes through the cervical spine, which transmits signals via nerve roots to the arms, hands and parts of the face. Blood vessels also run through the vertebrae to supply the brain with blood.
Common conditions and diseases
Pain in the cervical spine is common and can be caused by muscle tension, herniated discs, osteoarthritis or whiplash. Incorrect posture and prolonged sitting are common triggering factors.
Examination and diagnosis
Diagnosis of cervical spine problems includes clinical examination, neurological tests and sometimes X-ray, CT or MRI of the cervical spine. It is important to assess both mobility and nerve involvement.
Relevant symptoms
- Pain in the neck and shoulders
- Stiffness and reduced mobility
- Headache from the neck area
- Numbness in the arms or fingers
- Dizziness or balance problems
Related conditions and diagnoses
- Herniated disc in the cervical spine
- Cervical spondylosis (neck osteoarthritis)
- Whiplash injury
- Neck lock
- Cervicogenic headache