Blood fats have several important functions in the body. Among other things, they help transport energy to the cells and are involved in the formation of new cells and hormones. There are several different types of blood fats, the two most common of which are triglycerides and cholesterol.
Triglycerides are the most common form of fat in the food we eat and serve as an important source of energy. If energy intake exceeds the body's needs, the excess is converted to triglycerides, which are stored in the liver and adipose tissue. They can then be released when the body needs energy.
Cholesterol is partly supplied through the diet, but is also formed in the liver, and is then transported into the blood. Cholesterol is transported in the form of lipoproteins and is often divided into two main types: HDL ("good cholesterol") and LDL ("bad cholesterol"). LDL cholesterol contributes to atherosclerosis, while HDL has a protective effect by transporting excess cholesterol away from the vascular system.
If the balance between different blood fats is disturbed, or if the levels become too high, the risk of atherosclerosis increases and thus also the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack and stroke.
Hyperlipidemia means that both triglyceride and cholesterol levels are elevated. Elevated levels of cholesterol alone are called hypercholesterolemia and are the most common and important blood fat disorder. LDL cholesterol can often be lowered through lifestyle changes, such as dietary changes and regular physical activity. In some cases, this is not enough and drug treatment may then be necessary.
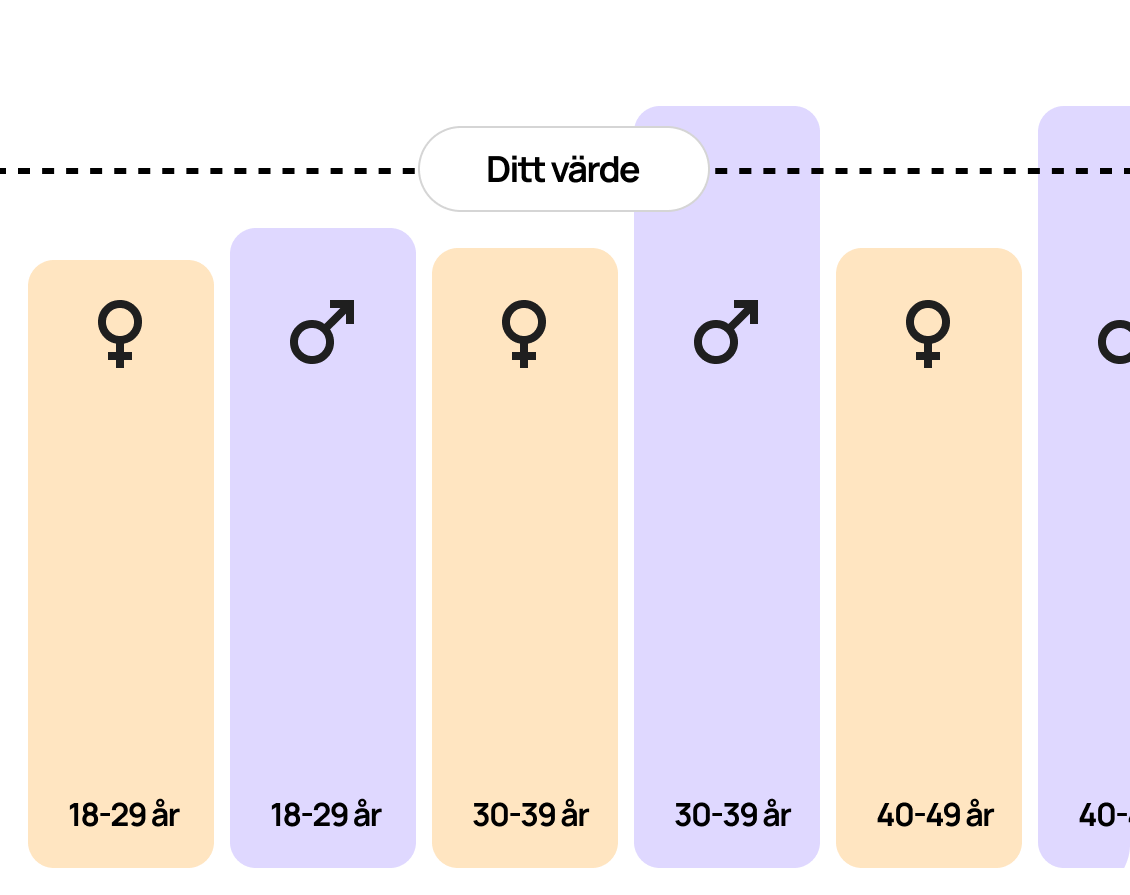
Target values for blood fats are individual and are based on the overall risk of cardiovascular disease, where factors such as previous illnesses and heredity are taken into account.
Get insight into your blood lipids
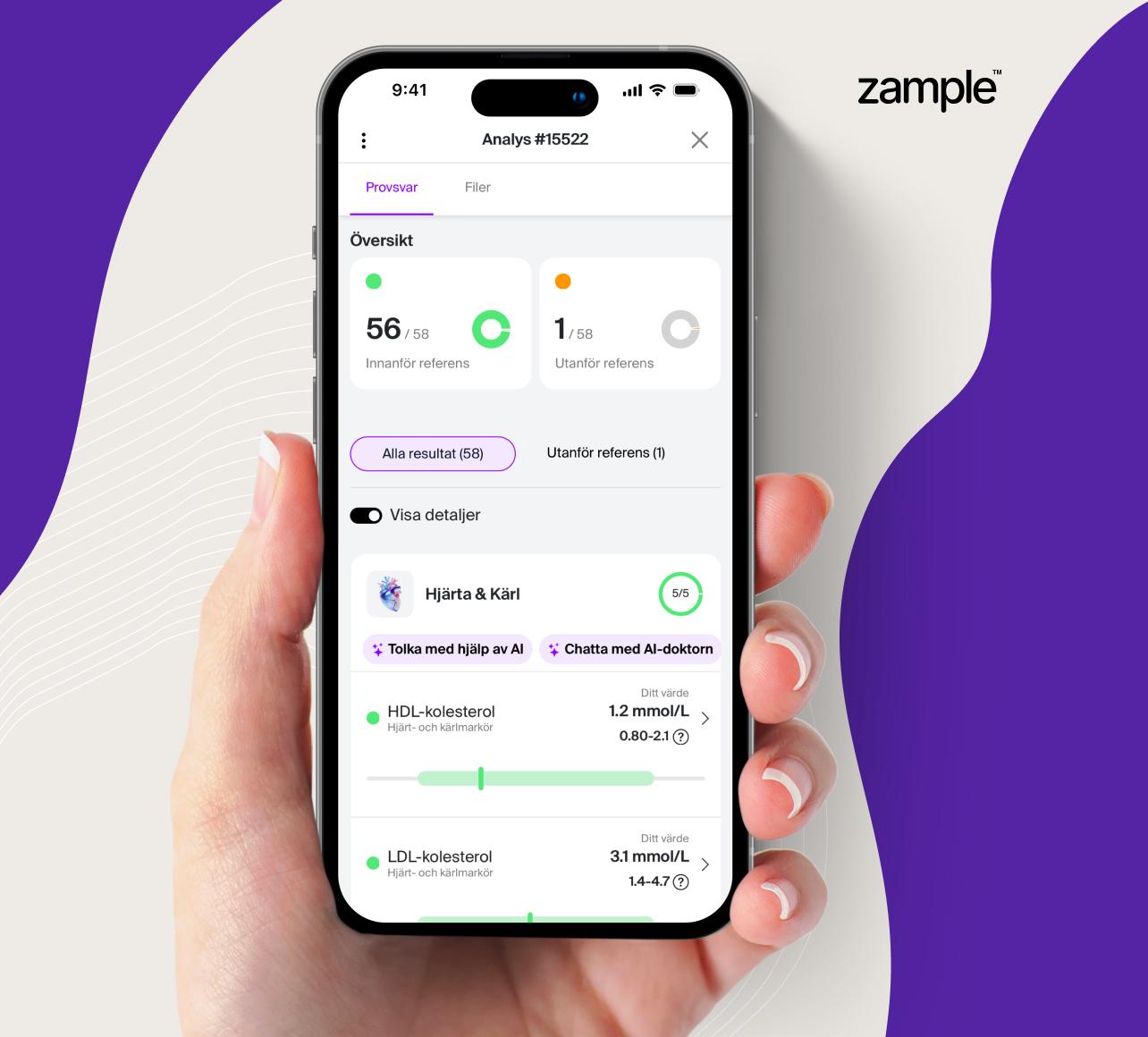
To get a picture of or follow your blood lipids over time, for example after changes in your lifestyle, we recommend that you carry out an analysis of the lipid profile. In this package analyzer as the most important blood lipids that can provide a picture of your current risk and guide future recommendations.
By checking your blood lipids, you can know that your values are within the desired range and that you have the conditions for continued healthy and vibrant health.
Blood lipids included in the blood test
- HDL cholesterol: The "good" cholesterol that protects against cardiovascular disease by transporting excess cholesterol away from the blood vessels.
- LDL cholesterol: The "bad" cholesterol that can form plaques in the blood vessels and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Total cholesterol: The total amount of cholesterol in the blood, including HDL and LDL cholesterol.
- Triglycerides: Fatty substances that are stored in fat cells and affect cardiovascular health.
- Non-HDL cholesterol: All lipoproteins that are not "high-density lipoproteins" (HDL), that is, low-density lipoproteins (LDL), very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), and other lipoproteins that can be atherogenic (promote the formation of plaques in the blood vessels).