Quick version
The throat is a complex and important structure for breathing, swallowing, speech and protection of central body functions.
- Contains airways and digestive tracts as well as blood vessels and nerves
- Has immune function through lymph nodes and tonsils
- Pain is often caused by infections or muscle tension
- Examined by palpation, mirroring and imaging
- Common diagnoses include tonsillitis, laryngitis and nodules
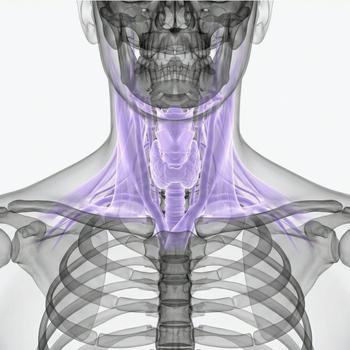
What is the throat?
The throat is the area between the head and the chest. It contains the trachea, esophagus, larynx, pharynx, tonsils, large blood vessels, and nerves such as the vagus nerve. The throat is also home to important lymph nodes and protective muscles.
Anatomy and structure
The throat consists of several layers: skin, muscles, blood vessels, airways, esophagus, and spine. The larynx and pharynx are central to breathing and voice. The carotid artery and jugular vein run in front of it.
Functions and systems
The throat serves as a passage for air to the lungs and food to the stomach. It protects nerves and blood vessels, enables voice production and is an important part of the immune system via the tonsils and lymph nodes.
Muscles and movements
The neck muscles control the movements of the head and help when you swallow and speak. The most important neck muscles are the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius. The muscles are easily affected by tension during stress or incorrect posture.
Common conditions and diseases
Throat pain can be due to infections (e.g. throat flu), muscle tension, swollen lymph nodes or problems with the thyroid gland such as hypothyroidism. Other causes may include tumors, laryngitis, or throat irritation.
Examination and diagnosis
Doctors visually inspect the throat, feel for lymph nodes, and may use mirrors or endoscopes to view the throat and vocal cords. If necessary, samples are taken or imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT or MRI of the throat are performed.
Relevant symptoms
- Sore throat
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Hoarseness
- Difficulty swallowing
- Lump in the throat
Related conditions and diagnoses
- Fluffy throat (tonsillitis)
- Laryngitis
- Mononucleosis
- Thyroid diseases
- Tense neck muscles