Quick version
The bile ducts are central to digestion and help the body eliminate waste products. Problems with the bile ducts can lead to pain, jaundice, and other serious conditions that require medical evaluation.
- The bile ducts transport bile from the liver and gallbladder to the intestines
- Bile breaks down fat in the food we eat
- Bile duct diseases can cause pain and jaundice
- Examinations include blood tests, ultrasound, MRI, and ERCP
- Common diseases include gallstones and cholangitis (inflammation)
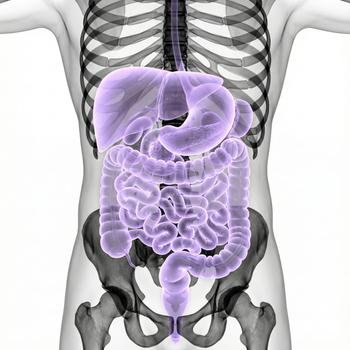
What are the bile ducts?
The bile ducts are a network of channels that transport bile — a fluid produced in the liver. Bile contains bile salts, bilirubin, and cholesterol, which help break down fats from the food we eat and remove waste products from the body. The bile ducts are divided into intrahepatic bile ducts (inside the liver) and extrahepatic bile ducts (outside the liver).
Anatomy and structure
The bile ducts form small channels in the liver that merge into larger ducts, eventually forming the hepatic duct and the common bile duct (ductus choledochus). These two ducts connect the liver and gallbladder to the duodenum.
Function and importance
The main function of the bile ducts is to transport bile to the intestine, where it helps break down and absorb fat. They also serve as a pathway for waste substances that the body needs to eliminate.
Common conditions and diseases
Pain in the bile ducts can be caused by various conditions. Common causes include gallstones (cholelithiasis) that block the ducts, infection (cholangitis), and tumors or strictures in the bile ducts. These conditions can lead to abdominal pain, jaundice and digestive problems.
Examination and diagnosis
To assess liver function, blood tests that measure liver values are needed. To diagnose bile duct diseases, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdomen, or endoscopic examination is often required in addition to blood tests.
Relevant symptoms
- Pain in the upper right part of the abdomen
- Jaundice (yellow skin and eyes)
- Dark urine and pale stools
- Fever and chills during infection
- Nausea and vomiting
Related conditions and diagnoses
- Gallstones (cholelithiasis)
- Cholangitis (inflammation of the bile ducts)
- Bile duct cancer (cholangiocarcinoma)
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas)
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis