Quick version
The abdomen is a central area that contains many vital organs with functions in digestion, detoxification and reproduction.
- Contains the stomach, intestines, liver, kidneys and other important organs
- Divided into quadrants for diagnosis
- Pain can have many causes
- Examined with palpation, blood tests and imaging
- Common diagnoses include IBS, appendicitis and gallstones
What is the abdomen?
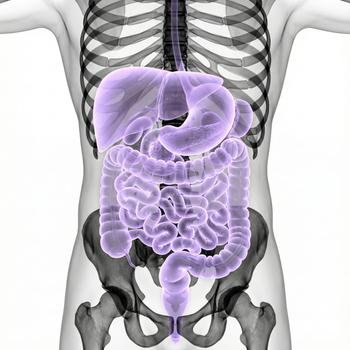
The abdomen, or abdomen, is the body cavity between the thorax and the pelvis. It is surrounded by the abdominal wall and contains organs of the digestive system, urinary tract, and reproductive and immune systems.
Anatomy and structure
The abdomen is divided into upper, middle, and lower parts and four quadrants. It is surrounded by abdominal muscles, fatty tissue, and the peritoneum (peritoneum), which protects the internal organs in the abdomen.
Organs in the abdomen
The abdomen contains the gastrointestinal tract, which includes the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. The liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, urinary bladder, and internal genital organs depending on gender are also located in the abdomen. These work together for nutrient absorption, detoxification, and reproduction.
Function of the abdomen
The abdominal organs are responsible for digestion, nutrient absorption, blood purification, urine production, immune functions, and hormone signaling. The abdomen is also a place where many diseases can occur.
Examination of the abdomen
In the case of abdominal complaints, palpation, auscultation, blood tests, and imaging diagnostics such as ultrasound, MRI of the abdomen, or computed tomography are used. The examination is directed by the location and nature of the symptoms.
Common causes of abdominal pain
Abdominal pain can be due to infections, inflammation, blockages, bleeding, tumors or functional disorders such as IBS. The exact cause is determined through clinical assessment together with a doctor.
Relevant symptoms
- Pain or cramps in the stomach
- Swelling or bloating
- Nausea and vomiting
- Changed bowel habits
- Fever with infection
Related conditions and diagnoses
- Appendicitis (appendicitis)
- Gallstones
- Kidney stones
- Stomach ulcer
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Cirrhosis of the liver