Quick version
The uterus is a central part of the female reproductive system. The organ plays a crucial role in fertility and pregnancy, and its function is regulated by hormonal cycles.
- Its tissue consists of three layers
- Influenced by estrogen and progesterone
- Common conditions include fibroids, PCOS, and endometriosis
- Examinations are often performed through gynecological ultrasound
What is the uterus?
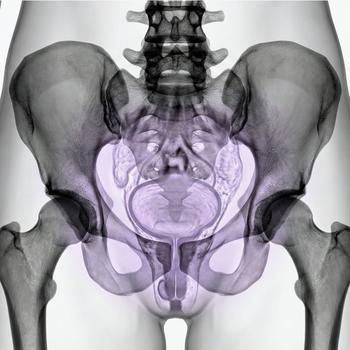
The uterus is a muscular organ located in the lower abdomen of women, between the bladder and the rectum. Its main function is to carry and nourish the fetus during pregnancy.
Anatomy of the uterus
The uterus is pear-shaped and divided into the uterine body (corpus), the cervix, and the uterine cavity. Its walls consist of three layers: the endometrium (the inner lining), the myometrium (the muscular layer), and the perimetrium (the outer layer).
What is the function of the uterus?
The uterus has several functions before and during pregnancy as well as during childbirth. Its roles include enabling menstruation, receiving a fertilized egg, providing nourishment to the fetus during pregnancy, and helping the body deliver the baby through muscle contractions.
The function of the uterus is regulated by hormones
There is a clear connection between the function of the uterus and the hormones estrogen and progesterone. During the different phases of the menstrual cycle, these two hormones regulate the buildup and shedding of the uterine lining, preparing the body for a possible pregnancy each month.
Common conditions and disorders
Pain in the uterus can have several causes, such as endometriosis, fibroids, adenomyosis, or inflammation. Uterine cancer or hormonal imbalances can also cause pain, bleeding, or a feeling of pressure.
Examination and diagnosis
Examination of the uterus is usually performed through a gynecological exam and vaginal ultrasound. To obtain a clearer image of the structures within the uterus, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be conducted. A blood test can also be helpful in assessing hormonal status.
Relevant symptoms
- Menstrual pain or irregular periods
- A feeling of pressure in the pelvis
- Spotting or bleeding between periods
- Difficulty getting pregnant
- Pain during intercourse
Related conditions and diagnoses
- Endometriosis
- Fibroids
- Adenomyosis
- Uterine cancer
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)