Quick version
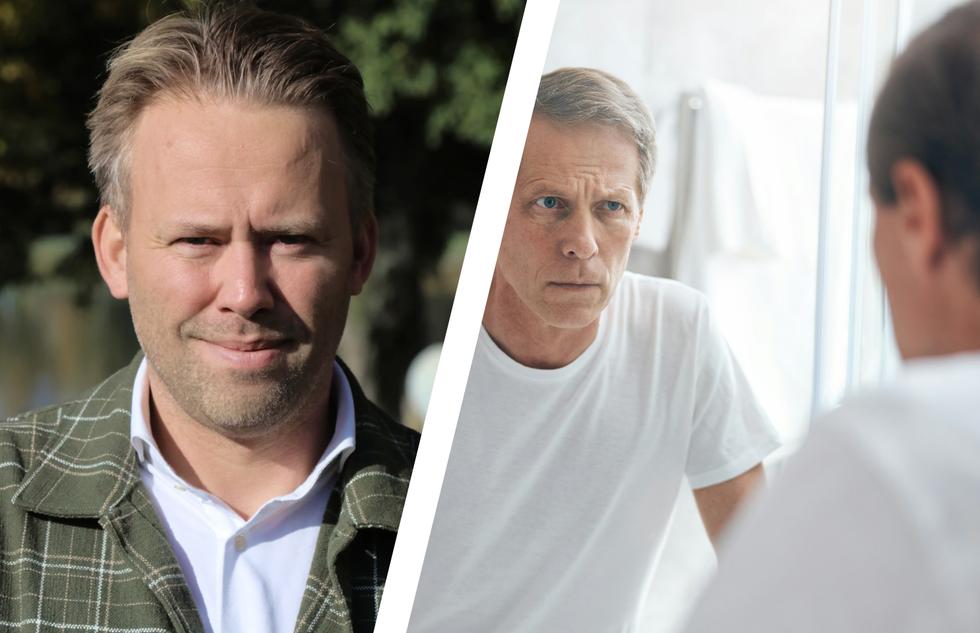
Impotence after prostate cancer – a common problem
One of the most common consequences of prostate cancer surgery is reduced sexual function. Many men have difficulty getting or maintaining an erection, which can affect both self-esteem and quality of life. The underlying cause of this is often that the nerves around the prostate itself, which control blood flow to the penis, are damaged during the procedure during prostate surgery.
- Every week we see men seeking help for erection problems - it is much more common than most people think, says Erik Lind, chief physician and medical director at Testmottagningen.se.
Tips if you are going to undergo prostate surgery: Talk to your doctor about the risk of erection problems before the operation, there are treatments and rehabilitation programs that can improve the prognosis afterwards.
Hormonal causes: "It can be treated"
The older we get, the lower the testosterone levels become. This is because testosterone in the body naturally decreases with increasing age and as a result, both sex drive and erection ability can be affected.
- Typical symptoms: fatigue, depression, weight gain, reduced body hair and reduced sex drive.
- Often affects men over 60, but can already be seen in their 40s.
- Can be treated with testosterone replacement after examination by a doctor.
- Many who test their values, including testosterone, are depressed, tired and have low sex drive. In many cases, it is a testosterone deficiency that can actually be treated, explains Lind.
Studies show that up to 50% of men over 40 experience some degree of erectile dysfunction (Massachusetts Male Aging Study). You can easily test your testosterone levels via a blood test - either at a health center or via private health tests: get answers to your testosterone levels. The results can provide clear answers as to whether hormone levels are the cause of your problems.
Psychological causes play a big role
Even young men with good physical health can have erection problems – often due to purely psychological reasons:
- Performance anxiety
- Depression
- Stress
- Worry about not being enough
- Relationship problems
“We come into contact with men who are completely healthy physically, but who have major problems with their potency because they cannot relax or feel pressure to perform sexually,” says Lind. “It is not uncommon for men in their 30s and 40s to first order potency drugs online before even talking to a doctor. Many are ashamed – but daring to seek help is a first step towards feeling better, both physically and mentally,” he says. We experience that the problem has increased in society in recent years, and is getting worse with age. Being able to get – and maintain – an erection requires that you have sufficient blood flow to the penis. When the brain sends signals to the genitals during sexual stimulation, the blood vessels dilate and blood flows to – up to 25 times the normal volume. Diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS), spinal cord injuries or nerve diseases can impair communication between the brain and penis, these are factors that make it more difficult to get an erection. You should seek medical attention if: Testosterone deficiency is treated with testosterone replacement, usually as a gel, patch or injection. The treatment is started after a blood test and a medical evaluation, and is followed up regularly by a doctor to ensure effectiveness and minimize risks. - The most important thing is to get a correct diagnosis. With the right treatment, many can get back both their energy and sex drive, and their quality of life is improved, says Erik Lind.Blood vessel problems – more common in diabetes
Neurological diseases – affect nerve signals
When should you seek medical attention?
How to treat testosterone deficiency