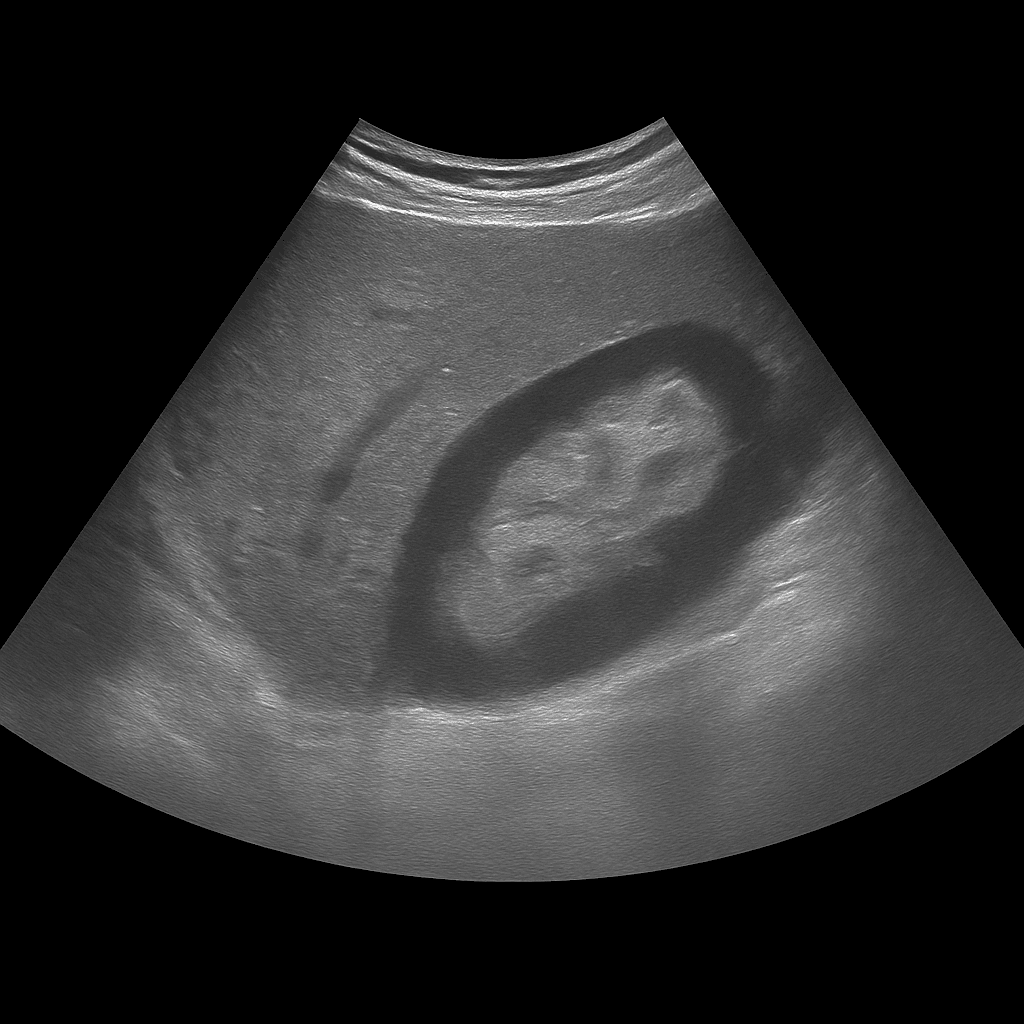
A kidney ultrasound is used to examine the size, shape, tissue structure and blood flow of the kidneys. The examination is performed by a specialist in radiology and provides detailed images in real time that can detect changes that affect kidney function or urine flow. It is used to investigate, among other things, kidney stones, cysts, fluid accumulation, infections or suspected tumors.
Ultrasound of the kidneys - for pain, urinary tract problems or altered blood tests
Ultrasound of the kidneys is recommended for symptoms such as flank pain, repeated urinary tract infections, blood in the urine or swelling in the body. It is also common for the examination to be performed when there are abnormal kidney values in blood tests (for example, elevated creatinine or Cystatin C) to assess the appearance and drainage of the kidneys.
Unlike MRI and CT, which are often used for more advanced mapping or suspected tumors, ultrasound is the first-line method for functional and structural assessments. It can be performed without contrast media and shows the kidneys in real time – ideal for detecting stones, cysts or fluid accumulation without the risk of radiation.
Common symptoms and questions
- Pain in the side or lower back (flank pain).
- Blood in the urine or recurrent urinary tract infections.
- Suspected kidney stones or obstruction of the ureters.
- In case of elevated kidney values in blood tests.
- Swelling in the legs or around the eyes (signs of fluid retention).
- Follow-up after previous findings in the kidneys or urinary tract.
Conditions that can be detected with an ultrasound examination of the kidneys
- Kidney stones or outflow obstruction in the ureters.
- Fluid accumulation (hydronephrosis) due to blockage in the urinary tract.
- Kidney cysts or multiple cyst formations.
- Changes in the kidney parenchyma in chronic kidney disease.
- Kidney infection (pyelonephritis) with swelling of the kidney tissue.
- Tumor or suspicious mass in the kidney that requires further investigation with MRI or CT.
How an ultrasound of the kidneys is performed
The examination is performed while you lie on your back or side. A gel is applied to the skin and the doctor moves the ultrasound probe over the area where the kidneys are located. Both kidneys are assessed in longitudinal and cross-sectional views, and if necessary, the bladder is also examined to assess any impact on urine flow. The examination is painless and usually takes 15–20 minutes. You do not normally need to fast or prepare, but sometimes the doctor may ask you to drink water before the examination so that the bladder is slightly full.
Order an ultrasound examination of the kidneys - get a report and recommendation from a doctor
The images are reviewed by a specialist in radiology who draws up a written medical report. The answer is delivered digitally within a few working days and can be shared with your treating doctor for further investigation or treatment. If necessary, the findings can be followed up with MRI or CT for further mapping.