Quick version
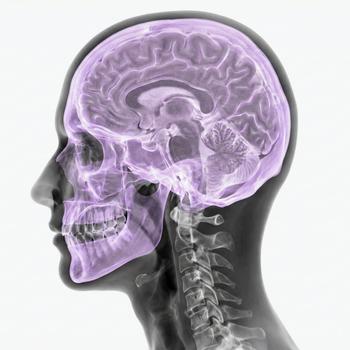
The skull base is an anatomically complex and functionally important part of the cranium with several sensitive structures.
- The skull base forms the base of the skull and supports the brain.
- It contains important openings for nerves and vessels.
- Injuries such as fractures can cause serious symptoms.
- Imaging is used for diagnosis.
- Treatment may include surgery or monitoring depending on the condition.
What is the skull base?
The skull base consists of several bones that form a complex structure with cavities (foramina) through which nerves and vessels pass, it forms the bottom of the skull. The skull base supports the underside of the brain and separates the brain from the facial and neck structures. The skull base is a critical part in both protection and communication between the brain and the rest of the body.
Anatomical parts
The anterior, middle, and posterior cranial fossa are the three fossae into which the skull base is divided. It contains several bones such as the frontal bone (os frontale), the sphenoidal bone (os sphenoidale), the temporal bone (os temporale), and the occipital bone (os occipitale). Important openings such as the foramen magnum, the foramen ovale, and the optic canal are located here.
Function and significance
The skull base has both a supportive and protective function. It supports the weight of the brain, protects the lower parts of the brain, and allows passage for cranial nerves, spine, and blood vessels. The skull base is sensitive to trauma or disease due to its complex structure.
Common conditions in the skull base
The skull base can be affected by injuries or diseases such as skull base fractures, tumors, congenital malformations, and infections. Injuries in the area can affect the cranial nerves and cause serious neurological symptoms.
Skull base fracture
A fracture in the skull base often occurs as a result of severe trauma, such as falls or traffic accidents. Signs may include bleeding from the ears/nose, bruising behind the ears (Battle's sign), and leakage of cerebrospinal fluid. Skull base fractures often require hospitalization and observation.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis is made with imaging diagnostics such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The treatment you receive depends on the condition and may include surgery, antibiotics, monitoring, or neurosurgical intervention for pressure or nerve damage.
Relevant symptoms
- Headache
- Visual disturbances
- Hearing loss or tinnitus
- Balance difficulties
- Bleeding from the ears or nose
- Neurological deficits
Related conditions and diagnoses
- Skull base fracture
- Skull base tumor
- Infections in the skull base (e.g. osteomyelitis)
- Congenital malformations
- Intracranial pressure