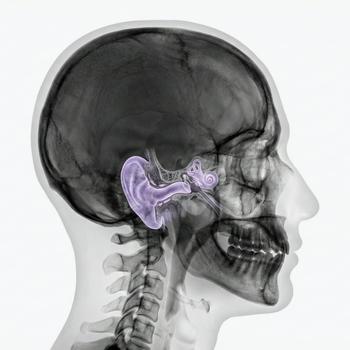
Quick version
The ear canal is the body's sound channel to the eardrum and plays an important role in hearing function.
- Conducts sound from the outer ear to the eardrum
- Consists of cartilage and bone with protective earwax
- Protects against dirt, bacteria and moisture
- Can suffer from inflammation, wax plugs or irritation
- Important for normal hearing
What is the ear canal?
The ear canal, also called the external auditory canal (meatus acusticus externus), is a canal that is about 2.5 centimeters long, it connects the outer ear with the eardrum. The outer part of the ear canal consists of cartilage, while the inner part is surrounded by bone.
Function of the ear canal
The main task of the ear canal is to transport sound waves to the eardrum. It naturally amplifies certain frequencies and protects the inner ear from dirt, bacteria and water.
Anatomical structure
The ear canal is divided into two parts. The inner part consists of bone and has thinner skin without hair or glands. The outer third consists of elastic cartilage and is covered by skin with hair and glands that produce earwax.
Earwax and Protection
Earwax (cerumen) is naturally produced in the outer part of the ear canal. It acts as a protection against bacteria, traps dirt and prevents water from entering the eardrum.
Common Problems
The ear canal can be affected by several conditions such as wax plugs, infections or foreign objects. It is important to be careful when cleaning the ear canal because excessive cleaning with cotton swabs can damage the skin and cause irritation or infection.
Examination of the ear canal in case of problems
Examination of the ear is justified in the case of a number of symptoms and conditions that may indicate infection, damage or other disturbances in the anatomy or function of the ears. Ear examinations are primarily performed using an otoscope – an instrument with a light and magnifying lens that allows you to look into the ear canal and eardrum. MRI examination of the ear canal is used to show detailed images of the inner ear, auditory nerve and surrounding structures – something that is not visible with regular otoscopy or X-ray.
Relevant symptoms
- Hearing loss
- Itching or irritation
- Pain in the ear
- Pressure or fullness
- Fluid or pus from the ear
Related conditions and diagnoses
- Wax plug (cerumen)
- Otitis externa (inflammation of the ear canal)
- Eczema in the ear canal
- Foreign body in the ear
- Ear canal exostosis (bone formation from exposure to cold water)