Quick version
Summary
The aorta is the body’s largest artery and plays a central role in the circulatory system. Its function is absolutely crucial for supplying the body’s organs with oxygen-rich blood.
- Transports blood from the heart to the body
- Divided into the ascending aorta, aortic arch, and descending aorta
- Diseases and injuries related to the aorta can be life-threatening
- Diagnosis is often made using ultrasound, CT, or MRI
- Common symptoms include sudden pain, shortness of breath, and changes in blood pressure
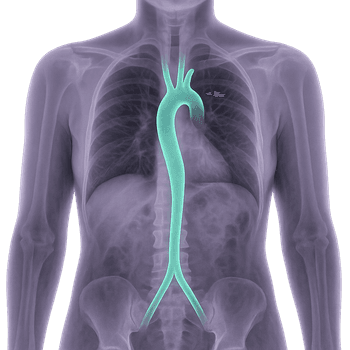
What is the aorta?
The aorta is the body’s largest artery, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and dividing into several branches that supply different parts of the body with blood. The aorta consists of several sections and is anatomically divided into the ascending aorta (ascendens), the aortic arch (arcus aortae), and the descending aorta (descendens), which continues through the chest and abdomen. Each section has unique branches that supply specific organs and tissues with blood.
Function
The main function of the aorta is to transport oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the body’s various organs. The walls of the aorta also contain elastic fibers that help absorb pressure variations between heartbeats, maintaining blood pressure and ensuring a steady blood flow.
Common conditions and diseases
Pain in the aorta itself is uncommon, but conditions such as aortic dissection, aortic aneurysm, and atherosclerosis can cause serious symptoms. These conditions require rapid diagnosis and treatment as they can be life-threatening.
Examination and diagnosis
Blood pressure measurements and cardiac examinations are performed to assess circulatory status and risk factors. To diagnose aortic diseases, imaging techniques such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be required.
Relevant symptoms
Seek emergency medical care if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Sudden, severe chest or back pain
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or fainting
- Pulse changes in arms or legs
- Blood pressure differences between the arms
Related conditions and diagnoses
- Aortic aneurysm
- Aortic dissection
- Aortic stenosis
- Hypertension
- Atherosclerosis