Quick version
The kidneys are the body's purification plants, regulating fluid, salts, and blood pressure.
- Filters the blood and produces urine
- Regulates fluid and electrolyte balance
- Produces important hormones
- Protects against infection and injury
- Common diseases include kidney stones and kidney failure
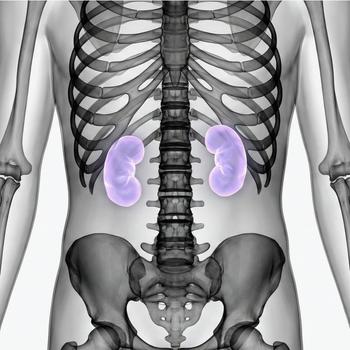
What is the kidney?
The kidney is a vital organ in the urinary system. We have two kidneys located on either side of the spine, just above the waist. The kidneys clean the blood of waste products and regulate the body's fluid, salt and acid-base balance. They are also important for the production of hormones that regulate blood pressure and the formation of red blood cells.
Anatomy and location
The kidneys are located in the back of the abdomen, near the lower part of the ribs. Each kidney is about 10–12 cm long and has an inner medulla and an outer cortex where filtration takes place.
Filtration of blood and urine production
Each kidney contains about one million nephrons – small filter units that clean the blood of waste products and excess fluid. The urine that is formed is led via the ureters to the bladder.
Regulation of blood pressure and fluid balance
The kidneys regulate blood pressure through the hormone renin and adjust fluid and electrolyte balance by reabsorbing sodium and water. This affects blood volume and thus the pressure in the vessels.
Hormonal production
The kidneys produce hormones such as erythropoietin (stimulates the formation of red blood cells) and convert vitamin D into its active form, which is important for calcium balance in the body.
Common diseases of the kidneys
The kidneys can be affected by infections, kidney stones, chronic kidney failure, cysts and autoimmune diseases that affect filtration. Regular blood and urine tests can detect these conditions at an early stage.
Relevant symptoms
- Fatigue and decreased urine output
- Swelling in the legs and feet
- Blood in the urine
- Back pain in the kidneys
- High blood pressure
Related conditions and diagnoses
- Acute and chronic kidney failure
- Kidney stones
- Nephritis and glomerulonephritis
- Urinary tract infection(UTI) that spreads to the kidneys
- Polycystic kidney disease