Quick version
Summary
The liver is the body’s largest internal organ with vital functions for metabolism, detoxification, and immune defense. It can be affected by a range of diseases, often with vague symptoms that are detected through blood tests and imaging.
- The liver weighs about 1.5 kg and has over 500 functions.
- It regulates blood sugar and metabolism.
- The liver detoxifies the body from medications, alcohol, and toxins.
- Common diseases include hepatitis, fatty liver, and cirrhosis.
- Symptoms may include fatigue, jaundice, and abdominal swelling.
What is the liver?
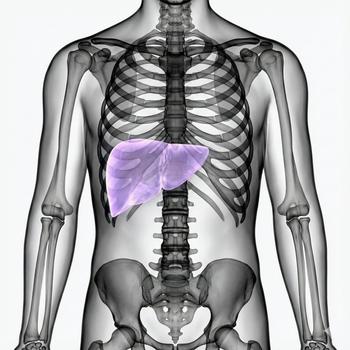
The liver is the largest internal organ in the human body and is located on the right side of the upper abdomen, just below the diaphragm. It weighs about 1.5 kg and has over 500 known functions, including filtering blood, producing bile, and storing nutrients.
The liver and its functions
The liver converts nutrients from the food we eat into energy, produces important proteins such as blood clotting factors, and stores vitamins and minerals. It also plays a crucial role in the body’s immune defense by neutralizing bacteria, viruses, and toxins that pass from the intestine into the bloodstream. Thanks to its versatility, the liver is essential for maintaining the body’s balance and health. Without the liver’s functions, energy metabolism, blood composition, and the body’s detoxification system would not function properly.
The liver and metabolism
By breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, the liver regulates the body’s energy balance. It controls blood sugar levels by storing and releasing glucose as needed.
Detoxification function
The liver is the body’s most important detoxification organ. It breaks down medications, alcohol, and toxins, which are then excreted through bile or urine.
Common conditions and diseases
Pain in the liver is rarely felt directly, but liver diseases can cause symptoms such as fatigue, yellowing of the skin (jaundice), and discomfort in the upper abdomen. Common conditions include fatty liver, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
Examination and diagnosis
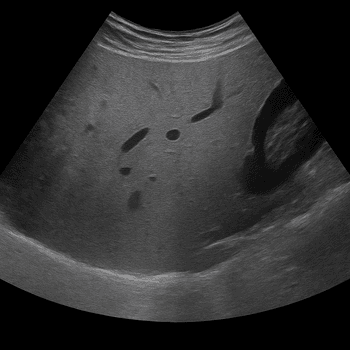
Liver diseases are investigated through blood test (liver function test), ultrasound of the liver, CT scans, and sometimes liver biopsy. These methods help identify inflammation, fibrosis, and tumors.
Relevant symptoms
- Fatigue
- Jaundice (yellow skin and eyes)
- Dark urine
- Pale stools
- Abdominal swelling (ascites)
- Nausea
Related conditions and diagnoses
- Hepatitis A, B, and C
- Fatty liver (NAFLD, alcohol-related)
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Liver cancer
- Biliary diseases