Quick version
The thorax protects vital organs and is central to breathing and upper body stability.
- Consists of ribs, sternum and thoracic spine
- Protects heart, lungs and large vessels
- Contributes to respiratory movements through muscles
- Pain can be due to anything from muscular to heart problems
- Is examined clinically and with imaging diagnostics if necessary
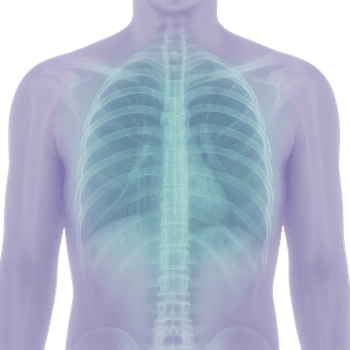
What is the thorax?
The thorax, or thorax, is the part of the skeleton that encloses the chest cavity. It consists of the breastbone (sternum), twelve pairs of ribs, and thoracic spine (thoracic vertebrae). The thorax serves as protection and plays a crucial role in breathing.
Anatomy of the thorax
The thorax is made up of both bone and cartilage. The ribs attach to the spine at the back and to the sternum at the front via cartilage. Between the ribs are intercostal muscles that help with breathing in and out. Heart and lungs are enclosed in the thoracic cavity.
Functions
The thorax has three main functions: it protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and large blood vessels, it enables breathing and provides attachment for respiratory and core stabilizing muscles. The thorax also contributes to posture and upper body movements.
Nervous system and blood supply
Nerves from the spinal cord run between the ribs and control the muscles and sensation in the chest wall. The blood supply comes from intercostal arteries and veins as well as large vessels such as the aorta and vena cava.
Common conditions and diseases
Pain in the chest can be caused by muscle tension, inflammation, rib fractures or heart and lung diseases. Muscle inflammation (myositis), costochondritis and pleurisy are examples of common causes.
Examination and diagnosis
Diagnosis of chest complaints is made through clinical examination, auscultation of the lungs and heart and, if necessary, ECG, X-ray, MRI of the chest, ultrasound or computed tomography. It is important to rule out serious conditions such as heart attack or pulmonary embolism.
Relevant symptoms
- Pain when breathing or coughing
- Pressure over the chest
- Shortness of breath
- Tenderness over the ribs
- Shaking pain with movement
Related conditions and diagnoses
- Rib fracture
- Costochondritis
- Pleuris
- Heart attack
- Muscle tension in the chest