Quick version
The prostate is an important part of the male anatomy and can be affected by several common conditions.
- The prostate produces fluid for semen.
- Common problems include enlarged prostate, inflammation, and cancer.
- Symptoms primarily affect the urinary tract.
- PSA testing and digital rectal examination are used for diagnosis.
- Treatments include medications, surgery, and monitoring.
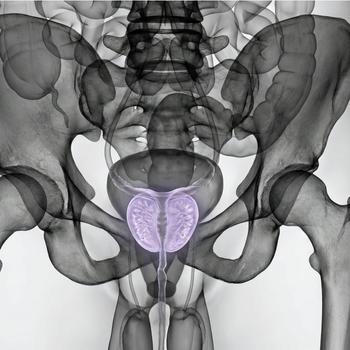
What is the prostate?
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland that is part of the male reproductive system, located just below the bladder and surrounding the upper part of the urethra. The prostate's main function is to produce some of the fluid that makes up semen.
Prostate Function
The prostate produces a nutrient-rich secretion that protects and improves sperm motility. During ejaculation, muscles in the prostate contract to help push the semen out through the urethra.
Common Prostate Diseases
The three most common conditions are benign prostatic hyperplasia (enlarged prostate), prostatitis (inflammation), and prostate cancer. These can cause varying symptoms and require different treatments.
Symptoms of prostate problems
Common symptoms include difficulty urinating, a weak urine stream, frequent urination, especially at night, and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area may also occur with prostate problems.
Diagnosis and tests
Doctors can examine the prostate via rectal palpation, PSA blood test, and sometimes ultrasound, biopsy, or a MRI scan of the prostate. The PSA test is often used to detect signs of prostate cancer but is not entirely specific.
Treatment of prostate diseases
Treatment varies depending on the diagnosis. An enlarged prostate is often treated with medication or surgery. Prostatitis is treated with antibiotics. Prostate cancer may require treatment with radiation, surgery, hormone therapy, or active monitoring.
Relevant symptoms
- Weak or interrupted urine stream
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Pain during urination or ejaculation
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Pelvic pain
Related conditions and diagnoses
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
- Prostatitis
- Prostate cancer
- Urinary retention
- Urinary tract infection