Quick version
The shoulder is a highly mobile joint that is susceptible to overload and injury, especially during repetitive motion or trauma.
- Consists of several joints and stabilizing muscles
- Provides great mobility in the arm
- Common complaints include pain, stiffness, and instability
- Injuries often occur during falls or repetitive motions
- Diagnosis requires a physical examination and sometimes imaging studies
What is the shoulder?
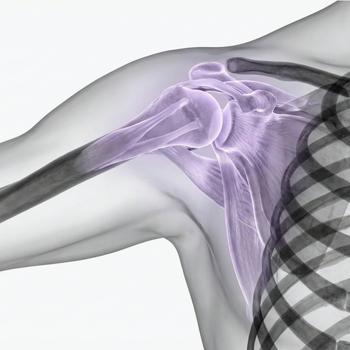
The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint that connects the upper arm (humerus) to the shoulder blade (scapula). It consists of several joints, muscles, and tendons that together provide great mobility but also make it vulnerable to injury.
Anatomy and structure
The shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is a shallow socket where the upper arm bone meets the shoulder blade. Around the joint is the rotator cuff – four muscles and their tendons – that stabilize the shoulder. The collarbone and the acromioclavicular joint (AC joint) are also part of the shoulder complex.
Movements and function
The shoulder performs flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, inward and outward rotation. The combination of the shape of the joint and the musculature makes it possible to raise the arms above the head and perform circular movements.
Nerves and blood supply
The shoulder is supplied by nerve branches from the brachial plexus, which control movement and sensation in the arm. The blood supply comes from arteries such as the axillary and subclavian.
Common conditions and diseases
Having pain in the shoulder can be due to overexertion, inflammation, injury or age-related changes. Common diagnoses include impingement, rotator cuff tear, frozen shoulder and dislocation (out of joint).
Examination and diagnosis
The diagnosis is based on a clinical examination, tests of mobility and strength and imaging diagnostics such as X-rays, ultrasound or MRI of the shoulder. Other testers can also be used if impingement or tendon problems are suspected.
Relevant symptoms
- Pain with arm movement
- Reduced mobility
- Weakness in the arm
- Clicking sound or instability
- Pain at night when lying down
Related conditions and diagnoses
- Impingement
- Rotator cuff tear
- Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis)
- Shoulder dislocation
- AC joint inflammation