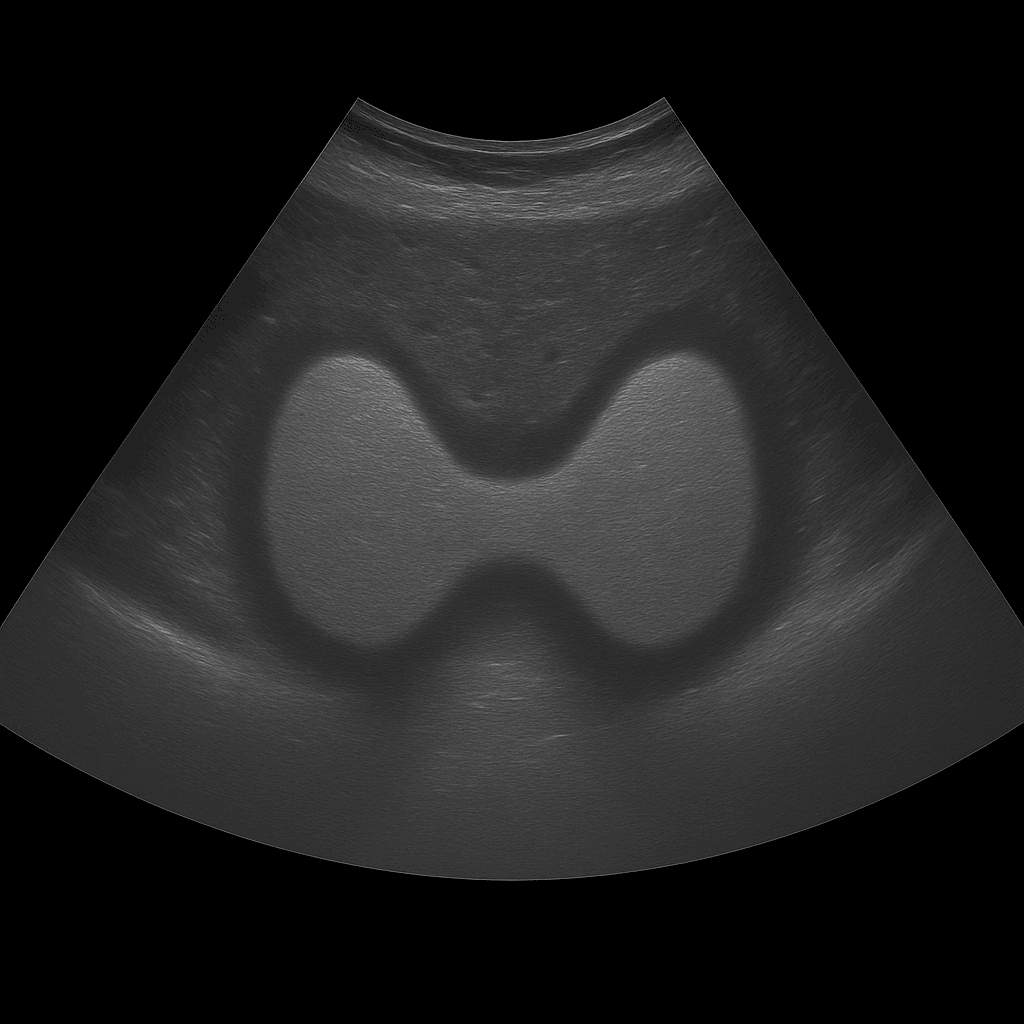
A thyroid ultrasound is used to assess the size, shape, tissue structure and any lumps or cysts of the gland. The examination is performed by a specialist in radiology and provides detailed real-time images of both lobes of the thyroid gland and the surrounding tissues in the neck. Thyroid ultrasound is used as the first-line method for investigating lumps, swelling, an enlarged thyroid gland or abnormal thyroid tests.
Thyroid ultrasound – for lumps, swelling or an enlarged thyroid gland
The examination is recommended for symptoms such as a lump in the neck, difficulty swallowing, a feeling of pressure, hoarseness or if goiter is suspected. It is also used to evaluate the structure of the thyroid gland in case of disturbed hormone values (TSH, T3, T4) or suspected autoimmune disease such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
Unlike MRI and CT, which are rarely used for the soft tissues of the thyroid gland, ultrasound provides a high-resolution and direct image of the tissue. Ultrasound can also distinguish between solid and fluid-filled lesions and is often used to guide fine-needle aspiration (puncture) of suspicious nodules. It is a rapid, radiation-free method that provides an immediate visual basis for diagnosis.
Common symptoms and questions
- Nodule, swelling or thickening in the neck.
- Enlarged thyroid gland (goiter) or irregular shape.
- Feeling of pressure, difficulty swallowing or hoarseness.
- Abnormal thyroid tests (TSH, T3, T4).
- Suspected Hashimoto's thyroiditis or other inflammation.
- Follow-up after previous findings of cysts, nodules or surgery.
Conditions that can be detected with thyroid ultrasound
- Nodules or cysts in the thyroid gland.
- Enlarged thyroid gland (goiter) with or without nodules.
- Inflammation in Hashimoto's thyroiditis or thyroiditis postpartum.
- Signs of benign or suspicious tumor changes.
- Changes in the structure of the tissue in autoimmune disease.
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck region that can affect the thyroid gland.
How a thyroid ultrasound is performed
The examination is performed while you lie on your back with your head slightly tilted back to expose the neck area. A gel is applied to the skin and the doctor moves the ultrasound probe over the thyroid gland. Both lobes and the isthmus (the connection between the lobes) are carefully assessed in longitudinal and cross-sectional views. If necessary, nearby lymph nodes in the neck can also be examined.
The examination takes about 10–15 minutes and is completely painless. No special preparation is required. If necessary, the doctor may recommend an additional fine needle biopsy (FNA) for tissue analysis.
Order an ultrasound examination of the thyroid – get a statement and recommendation from a doctor
The images are reviewed by a specialist in radiology who prepares a written medical report. The answer is delivered digitally within a few working days and can be shared with your treating doctor or endocrinologist for further follow-up. If necessary, the findings can be followed up with additional sampling or puncture.