Quick version
The ankle is an important joint for movement and balance. Injuries to the ankle can significantly affect daily life.
- Connects the lower leg to the foot
- Consists of the tibia, fibula, and talus
- Stabilized by strong ligaments
- Common ankle injuries include sprains and fractures
- Diagnosis is made through clinical examination and imaging
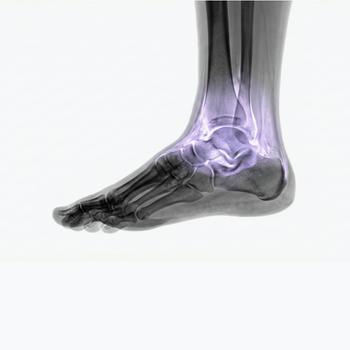
What is the ankle?
The ankle is the joint that connects the lower leg and the foot. The ankle consists of several bone structures, mainly the shinbone (tibia), the calf bone (fibula), and the talus (ankle bone).
Anatomy and location
The ankle is a hinge joint that allows us to bend the foot up and down. Around the ankle, on both the inside and outside, there are strong ligaments that stabilize and enable movement.
Function
The ankle bears a heavy load from the body’s weight and acts as a shock absorber during walking, running, and jumping. It makes it possible to move the foot in different ways, such as dorsiflexion (the foot bends upward, as when you lift your toes off the ground) and plantarflexion (the foot points downward, for example when standing on tiptoe).
Joint connections
The joint surfaces between the tibia, fibula, and talus form the ankle joint. On the outside of the ankle is the lateral ligament complex, and on the inside is the medial ligament, also known as the deltoid ligament. Together, these ligaments help support the ankle.
Development
The structure of the ankle is fully developed from the teenage years; after that, strength and stability can be improved through training and activity.
Common conditions and diseases
Pain in the ankle is often caused by sprains, ligament injuries, fractures, or inflammation. Sports injuries are a common cause of ankle problems.
Examination and diagnosis
The diagnosis is made through physical examination, function and movement tests, as well as imaging such as X-ray or MRI if needed. Book an MRI Ankle here and find out the cause of your ankle pain.
Relevant symptoms
- Swelling around the ankle
- Pain when bearing weight
- Stiffness
- Bruising
- Instability
Related conditions and diagnoses
- Ankle sprain
- Ankle fracture
- Ligament injury
- Arthritis
- Gout