Quick version
What can numbness and pain in the leg be caused by?
If you experience numbness, tingling, pins and needles, or loss of sensation in the leg, it is a sign that the nerves are not functioning properly. When this is combined with pain, it may indicate pressure, irritation, or injury to the nervous system or adjacent joints and structures.
Common causes
Sciatica
Sciatica occurs when the sciatic nerve becomes irritated or compressed, often due to a herniated disc or changes in the spine. Sciatica is often characterized by radiating pain from the lower back down into the leg.
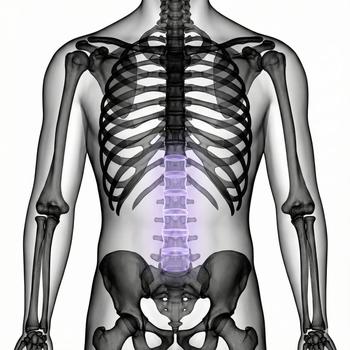
Herniated disc
A herniated disc means that a disc in the spine bulges out and presses on a nerve. This can cause symptoms such as pain, weakness, and numbness in the leg.
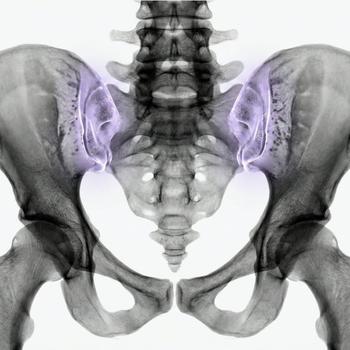
Sacroiliac joint inflammation (sacroiliitis)
Sacroiliitis is an inflammation of the pelvic joints (the sacroiliac joints). This can cause deep pain in the buttock and thigh, sometimes radiating down the leg.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis in the hip causes pain and stiffness. In some cases, osteoarthritis can also affect the nerve pathways and lead to reduced sensation in the leg.
Common symptoms of nerve problems
- Tingling or pins and needles in the leg
- Reduced sensation or numbness
- Dull or stabbing pain
- Weakness in the leg
- Pain that worsens with strain or certain movements
When should you seek medical care?
Seek medical attention if you have:
- Increasing numbness or weakness in the leg
- Sudden severe pain that does not improve with rest
- Numbness in the genital area or difficulty controlling urination and bowel movements
- Long-lasting symptoms that do not improve within a few weeks
Examinations and diagnosis
The doctor begins with a physical examination, assessing nerve function, muscle strength, and sensation. If the symptoms are severe or persistent, imaging may be needed to determine the cause. In cases of suspected herniated disc or sciatica, a MRI of the lumbar spine is performed, and for sacroiliitis or hip osteoarthritis, a MRI of the hip & pelvis may be relevant.
Treatment and self-care
Treatment depends on the cause but may include:
- Pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory medications
- Physiotherapy and exercises for the affected areas such as back, hip, and leg
- Injections into the joints in cases of sacroiliitis or osteoarthritis
- Surgery in cases of severe herniated disc or prolonged nerve compression
On your own, it is important to maintain good posture at work and ensure regular movement. Avoid sitting still for long periods.
Prevention
To prevent nerve compression, it is important to maintain strong back and core muscles, good posture, and avoid overloading the back and hips. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the pressure on joints and discs.